Fig. 3.
Intranasal insulin treatment reverses hippocampal dendritic injury and normalizes expression of selected brain function genes in EcoHIV-infected mice with neurocognitive impairment.
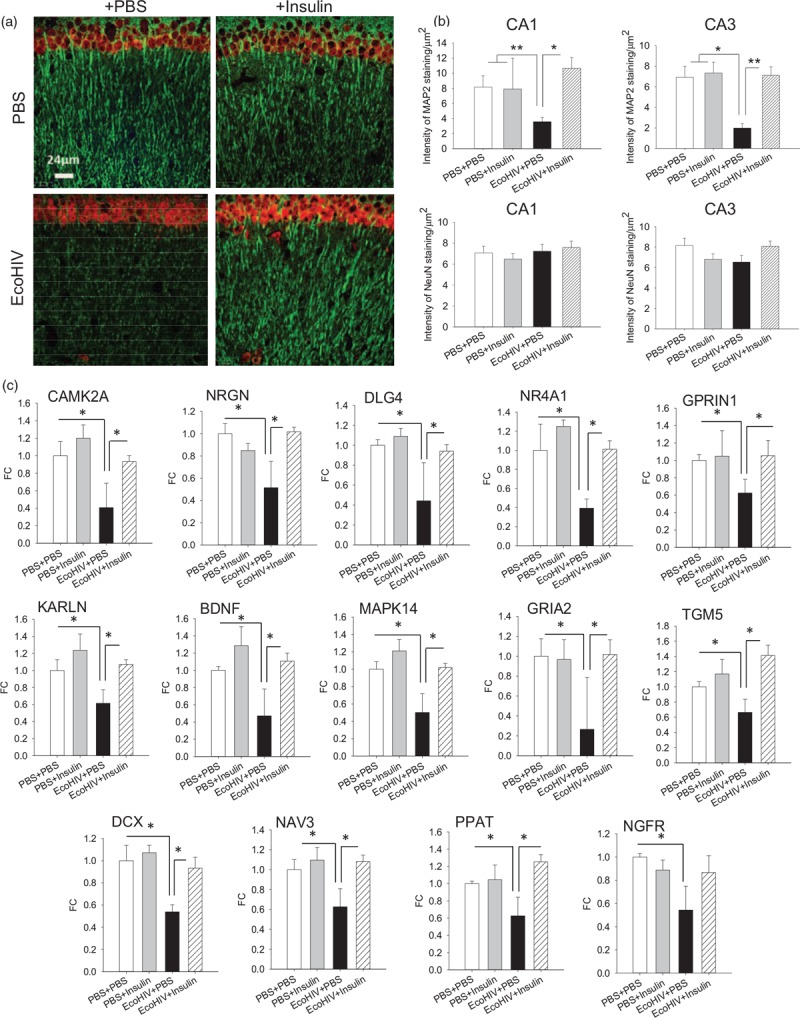
Brain specimens were from mice (three per variable) that completed behavioral testing in experiment shown in Fig. 2(a–c). (a) Representative confocal microscope images from the CA1 region of the hippocampus showing detection of neuronal dendritic [microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), in green] and nuclear [neuronal nuclear antigen (NeuN), in red] proteins; scale bar = 24 μm. (b) Quantification of MAP2 and NeuN staining in the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus; ∗P < 0.01, ∗∗P < 0.005. (c) Expression of selected brain function-related genes in brain tissues. Total brain RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed to complementary DNA (cDNA) as previously described [34]. The cDNAs were evaluated on custom TaqMan Array 96-Well Plates (ThermoFisher Scientific) according to manufacturer's instructions. The 88 genes represented in the arrays (Table S1) were chosen according to their published functions in synaptic plasticity, neuronal function, and brain metabolism. Fold change in gene expression relative to control (PBS intraperitoneally + PBS intranasal); ∗P < 0.05.
