Figure 2.
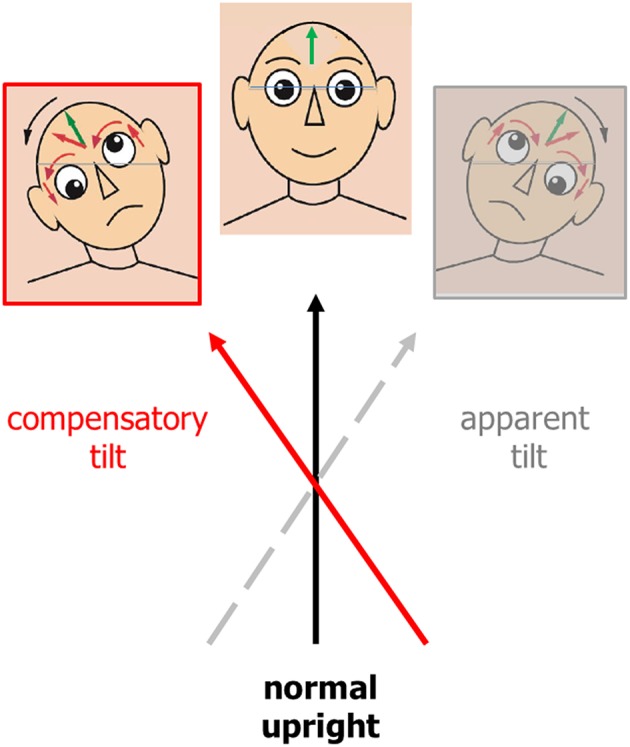
Ocular tilt reaction (i.e., triad of head tilt, vertical divergence, and ocular torsion of both eyes) and deviation of subjective visual vertical (green arrow = normal upright) represented as a “motor compensation” (in red) of a lesion-induced perception of eye-head tilt (in gray). The compensatory tilt is opposite in direction to the apparent tilt. Eyes and head are continuously adjusted to what the lesioned brain computes as being vertical.
