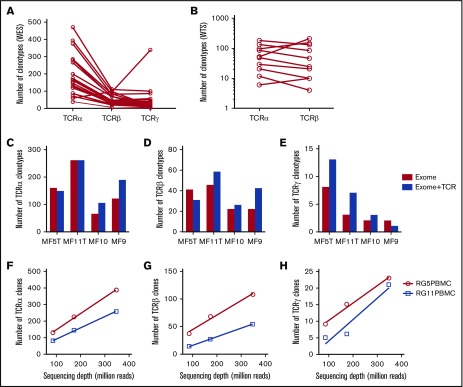
Figure 2.
Efficiency of WES probe capture and WTS protocols in the detection of CDR3 clonotypes in MF biopsies. All of the samples were sequenced using whole-exome probe capture (A) and WTS (B), and the number of clonotypes for TCRα, TCRβ, and TCRγ was determined for each sample, as indicated. The lines connect the results for the same sample. (C-E) The effect of TCR-specific probes. The capture was performed in 4 samples with whole-exome probes as in panel A (Exome) or with whole-exome probes combined with specific TCR capture probes (Exome+TCR) and sequenced, and the number of unique clonotypes for TCRα (C), TCRβ (D), and TCRγ (E) was determined, as in panel A. The addition of probes slightly increased the number of TCRγ clonotypes (P = .024, paired Student t test) but not the number of TCRα or TCRβ clonotypes. (F-H) The effect of sequencing depth on clonotype detection for TCRα (F), TCRβ (G), and TCRγ (H). Two samples of whole peripheral blood mononuclear cells were sequenced with WES at a maximum of 400 million reads, as in panel A. The samples do not reach saturation up to 348 million reads (∼800× sequencing depth).