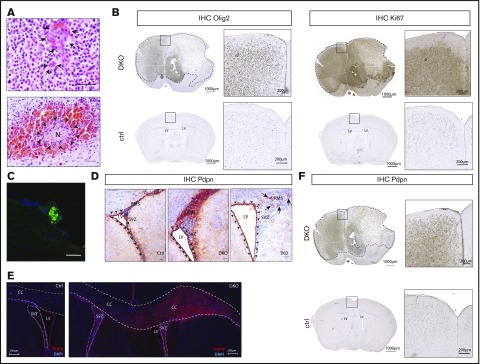
Figure 1.
Pten and p53 deletion in neural stem cells leads to development of gliomas with high PDPN expression and intratumoral platelet aggregates. (A) Histopathological features of gliomas developed in DKO mice. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Arrows indicate areas of microvascular proliferation. Arrowheads indicate a necrotic area (N) surrounded by hemorrhage. Scale bars, 50 µm. (B) OLIG2 and Ki67 expression (brown) in brain sections from a glioma-bearing DKO mouse and from a control (ctrl) tumor-free mouse detected by immunohistochemistry. The sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Dotted lines show tumor mass. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of CD41 (green) of a tumor area from a DKO mouse. Cellular nuclei are stained with DAPI and pseudocolored in blue. Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) PDPN expression (red) detected by immunohistochemistry of brain sections from: ctrl, DKO, and TKO mice euthanized 2 weeks after oil injection (for control), and tamoxifen-induced transgenes recombination (for DKO and TKO). The brain sections show the SVZ of the LV and RMS. Arrowheads indicate ependymal cells. Arrows indicate areas of residual PDPN expression in TKO mice. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Scale bars, 100 µm. (E) Immunofluorescence staining for PDPN of brain sections from a ctrl and DKO mouse euthanized 4 months after oil injection and tamoxifen-induced p53 and pten deletion, respectively. Cellular nuclei are stained with DAPI and pseudocolored in blue. Dashed lines show corpus callosum (CC). Dotted lines show SVZ. (F) PDPN expression (brown) in a brain section from a glioma-bearing DKO mouse and from a ctrl tumor-free mouse detected by immunohistochemistry. The sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Dotted lines show tumor mass.