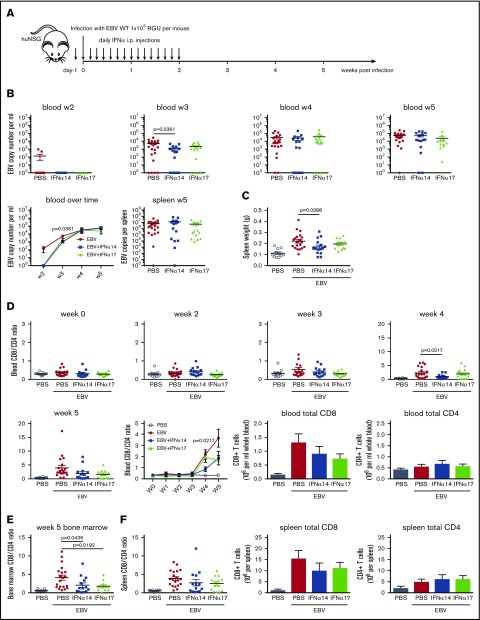
Figure 5.
Type I IFN injection transiently controls viral loads and attenuates CD8+T-cell expansion after EBV infection in huNSG mice. (A) huNSG mice were treated with either PBS, IFN-α14, or IFN-α17 for 15 consecutive days, starting 1 day before infection with 1 × 105 RGU EBV (schematic depiction). (B) Viral DNA loads were determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction in the blood over time and in the spleen at week 5. (C) Spleen weight was measured upon euthanization at week 5. (D) The ratio of CD8/CD4 T cells in the blood of huNSG mice was determined by using flow cytometry and monitored over time. Total CD8 and CD4 T-cell counts were determined at week 5. In the summary graphs over time (B,D), data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (E) The ratio of CD8/CD4 bone marrow T cells was determined by using flow cytometry. (F) The ratio of CD8/CD4 splenic T cells and total CD8 and CD4 T-cell numbers per spleen was determined by using flow cytometry at week 5. Data were pooled from 5 independent experiments (PBS, n = 20; IFN-α14, n = 15; IFN-α17, n = 15), and unpaired Student t tests were used.