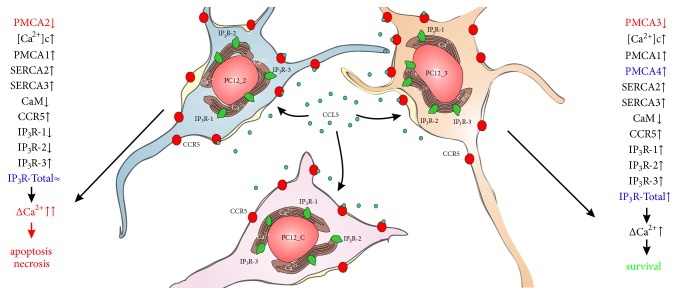
Figure 8.
Schematic presentation of CCL5 effect on PC12 cells. Downregulation of neurospecific PMCA2 or PMCA3 isoforms in differentiated PC12 cells generated two types of cell response: similar for both lines or characteristic for only one line. The common changes were increased cytosolic Ca2+ and, as a compensatory mechanism, upregulation of PMCA1 isoform, enlarged expression of SERCA2 and SERCA3, and diminished calmodulin amount [36, 40]. The levels of CCR5 and IP3R-3 proteins also increased, but the expression of IP3R-1 and IP3R-2 was lowered (present study). Interestingly, altered IP3R isoform composition did not change total IP3R protein in the _2 line, while it increased in the _3 line. Also in _3 cells, the amount of PMCA4 increased [36]. These subtle differences could have profound consequences after CCL5/CCR5 activation, since potency to restore the basal Ca2+ level in the _3 line appears to be higher than in the _2 line, which may be essential for the survival of the cell. Under prolonged Ca2+ signal in the _2 line due to reduction of the fastest isoform - PMCA2, the subsequent Ca2+-mediated processes could increase vulnerability to cell death. Abbreviations used: CaM, calmodulin; CCL5, chemokine C-C motif ligand 5; CCR5, receptor for CCL5; inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3); IP3R, IP3 receptor; PMCA, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase; SERCA, sarco/endoplasmic Ca2+-ATPase.