Figure 2. The kidney nephron is a rheostat for plasma volume.
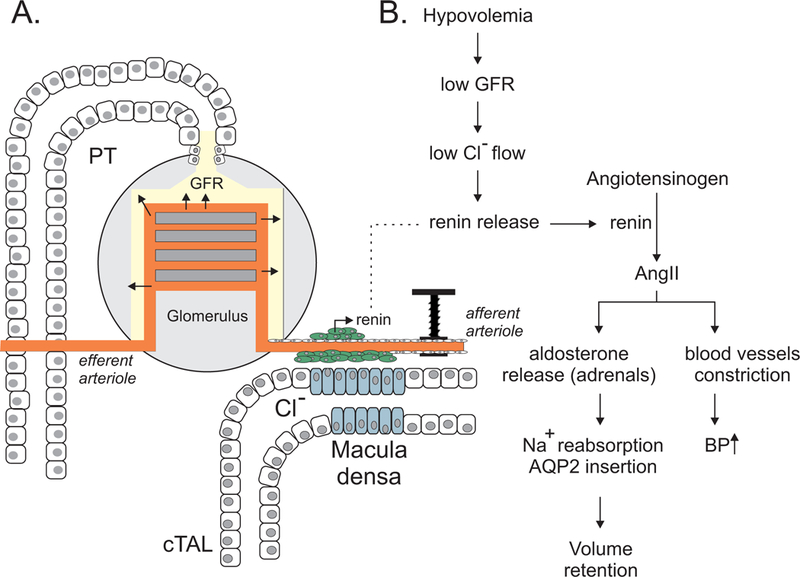
A, The ultrafiltration of blood into urine that begins in the glomerulus depends upon the wall pressure of afferent and efferent blood vessels. The rate of filtration at the glomerulus is one component that defines the amount of Cl− that flows at the macula densa. Macula densa cells serve as “sensors” of the amount of Cl−-containing filtrate that passes along the cortical thick ascending limb (cTAL). These cells relay information to specialized renin cells located in the wall of the afferent arteriole to release renin when necessary. B, Low blood volume (hypovolemia) ultimately results in renin release that acts on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Angiotensin II and aldosterone restore blood volume (and blood pressure) by affecting Na+ and water reabsorption (increased AQP2 insertion) and constriction of blood vessels.
