Figure 5. Ion and water transport in choroid plexus.
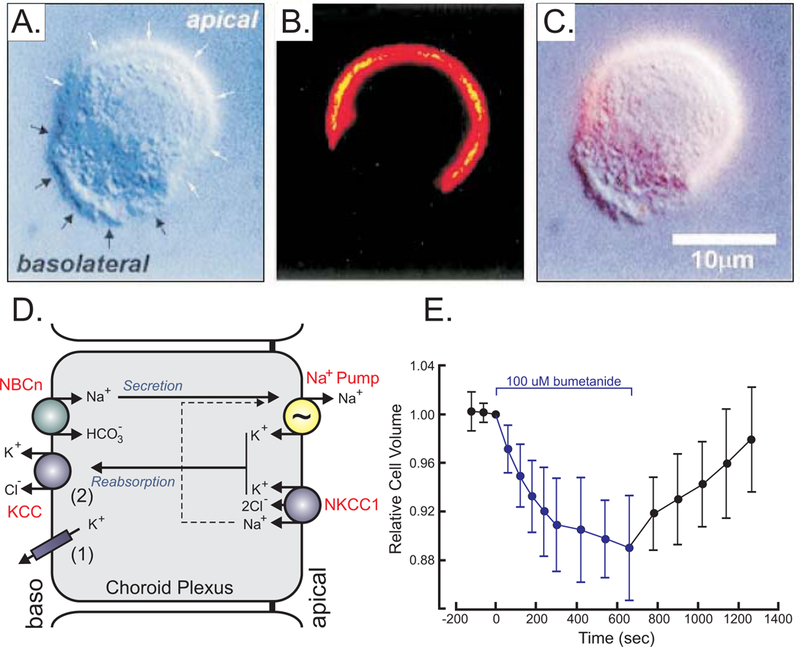
A, Mouse choroid plexus epithelial cell observed by Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy with white arrows identifying the apical and black arrows identifying the basolateral membrane, respectively. B, Fluorescent microscopy image of NKCC1 staining of the same cell using a secondary Cy3-conjugated antibody targeting a primary anti-NKCC1 antibody. C, Overlay of A & B showing presence of NKCC1 in apical membrane. D, Model of choroid plexus epithelial cell with apical Na+/K+-ATPase (pump) and NKCC1 and basolateral Na-bicarbonate cotransporter (NBCn) and K+ efflux mechanisms (KCC and K+ channels). E, Effect of bumetanide on relative cell volume, as measured by microscopy. Materials were taken with permission from (Wu, Delpire, Hebert & Strange, 1998).
