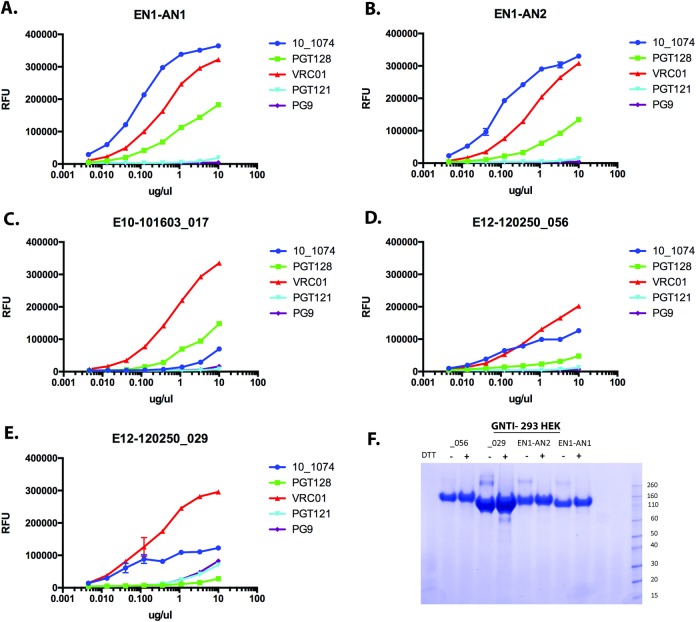
Fig 5. Comparison of bNAb binding to recombinant gp120 from native and inferred sequences.
Sequences encoding gp120 from inferred envelope sequences EN1-AN1, EN1-AN2 (panels A and B) or authentic virus sequences (Panels C-E) were expressed in in GNTI- 293 HEK cells. The proteins were captured onto the wells of microtiter dishes and used in a fluorescence immunoassay (FIA) to measure the binding to a panel of prototypic bNAbs. These included bNAbs to the V1/V2 domain (PG9), the CD4 binding site (VRC01), or overlapping sites dependent on amino acids and glycans at the stem of the V3 domain (PGT121, PGT128, 10–1074). Panels EN1-AN1 and EN1-AN2 are sequences of inferred common ancestors occurring before the appearance of sequences resistant to neutralization by autologous plasma (see Fig 1). The E10-101603_17 sequence represents a plasma derived sequence resistant to neutralization by autologous plasma, whereas the E12-120250_56 sequence represents provirus derived sequence sensitive to neutralization by autologous plasma. The E12-120250_029 sequence represents the earliest provirus sequence in the phylogenetic tree (Fig 1) and was sensitive to neutralization by autologous plasma. Panel F, represents an SDS-PAGE gel of recombinant proteins from EN1 stained with SimpyBlue (ThermoFisher) before and after reduction with dithiothreitol (DTT). In this panel, _056 and -029 indicates protein from sequences EN12-120250_56 and E12-120250_29, respectively.