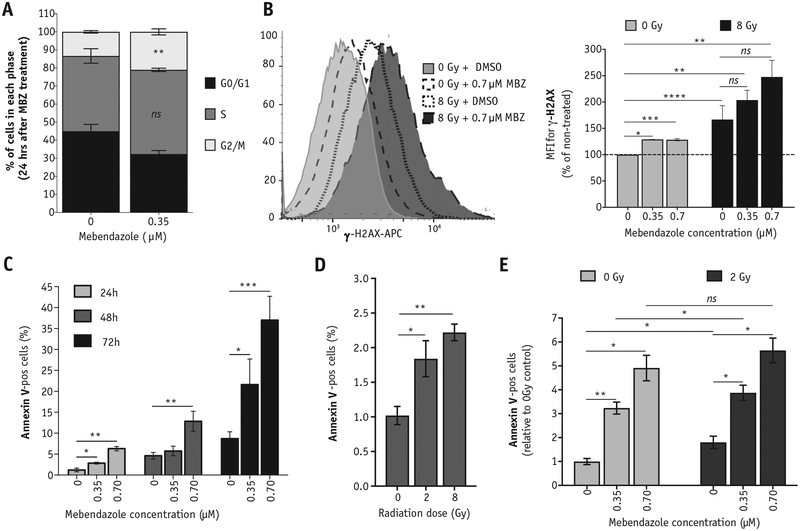
Fig. 4.
Exposure to MBZ induces double-strand breaks, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest. SUM159PT cells were treated with a single dose of MBZ at the indicated concentrations. (A) Cell cycle distribution was analyzed 24 hours after MBZ treatment using propidium iodide staining. (B) Twenty-four hours after MBZ treatment, cells were exposed to a single dose of IR (8 Gy). Thirty minutes after exposure to IR (or 24 hours after MBZ treatment), cells were removed and stained with anti-γ-H2AX-APC to determine the relative number of double-strand breaks (top). The MFI is plotted for the average of 3 independent experiments (bottom). Unpaired, 2-tailed t test: *P < .01, **P < .001, ***P < .0001, ****P < .00001, ns, not significant. (Bottom panel) Representative FACS histograms. (C-E) The percentage of cells staining positive for Annexin-V was determined via flow cytometry. (C) The percentage of Annexin-V-pos cells was determined at 24, 48, and 72 hours after MBZ treatment. (D) The percentage of Annexin-V-pos cells was determined at 24 hours after the indicated doses of radiation. (E) Cells were treated with the indicated doses of MBZ and, 24 hours later, exposed to 2 Gy. The percentage of Annexin-V-pos cells was determined 24 hours after irradiation. Paired, 2-tailed t test: ns, not significant, *P < .01, **P < .001. Abbreviations: FACS = fluorescence activated cell sorting; IR = ionizing radiation; MBZ = mebendazole; MFI = mean fluorescent intensity.