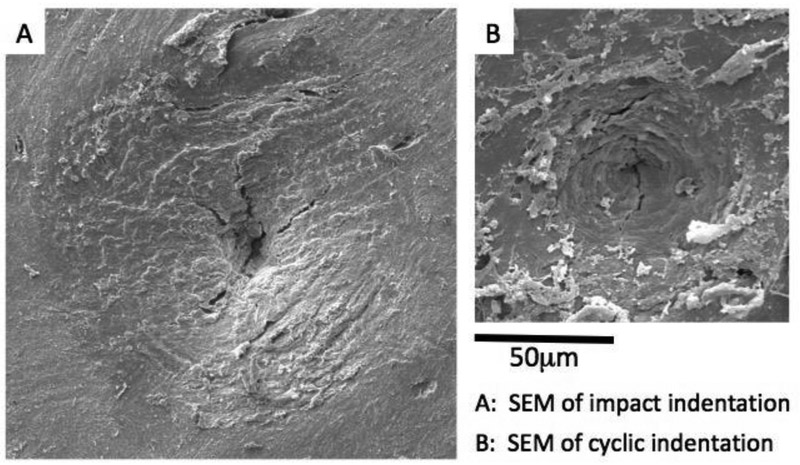
Figure 4:
Scanning electron micrographs of indented regions created by (A) impact indentation (OsteoProbe) and (B) cyclic indentation (BioDent) on an unprepared human bone surface. Both RPI methods result in damage including cracks and plasticity indicating the complex processes at the material level during the indentations (Images courtesy of Active Life Scientific).