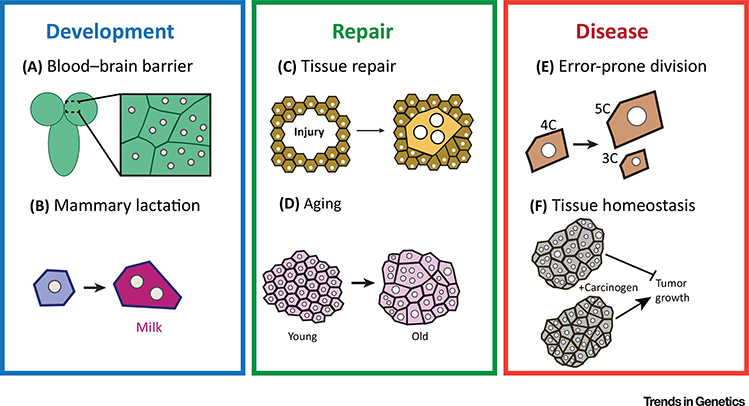
Figure 2. The functional significance of polyploidy in health and disease.
Illustrations of recent discoveries of polyploidy in health and disease. (A) Development and function of the blood brain barrier in Drosophila requires a balance of mono- and multinucleated polyploid cells generated by endocycle and endomitosis. (B) Mammary gland lactation requires polyploidization of secretory cells by endomitosis. (C) Wound-induced polyploidization occurs in Drosophila and vertebrate tissues to promote repair. (D) Polyploid cells arise with age and may help to compensate for cell loss. (E) Polyploid cells can retain the capacity to divide yet are susceptible to error-prone division resulting in aneuploidy. (F) Polypoid cells can also restrict tumor growth.