Fig. 2. The preparation and characterization of ferritin-rich HepG2 cell samples.
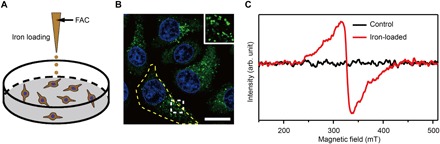
(A) Schematic view of the treatment to cultured cells. Following iron loading or no treatment, the HepG2 cells were examined for fluorescence images and EPR spectra, respectively. For the MI and TEM imaging, cell samples were treated through high-pressure freezing, freeze substitution, and sectioning. (B) Representative CFM image of ferritin structures (green) in iron-loaded HepG2 cells. The ferritin proteins were immunostained by anti-ferritin light chain antibody. The nuclei are indicated by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) in the blue channel. Inset displays magnified ferritin structures. The yellow dashed line outlines the contour of a cell. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) EPR spectra of control and iron-loaded HepG2 cells at T = 300 K. HepG2 cells, harvested by trypsinization, were fixed with paraformaldehyde and immersed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
