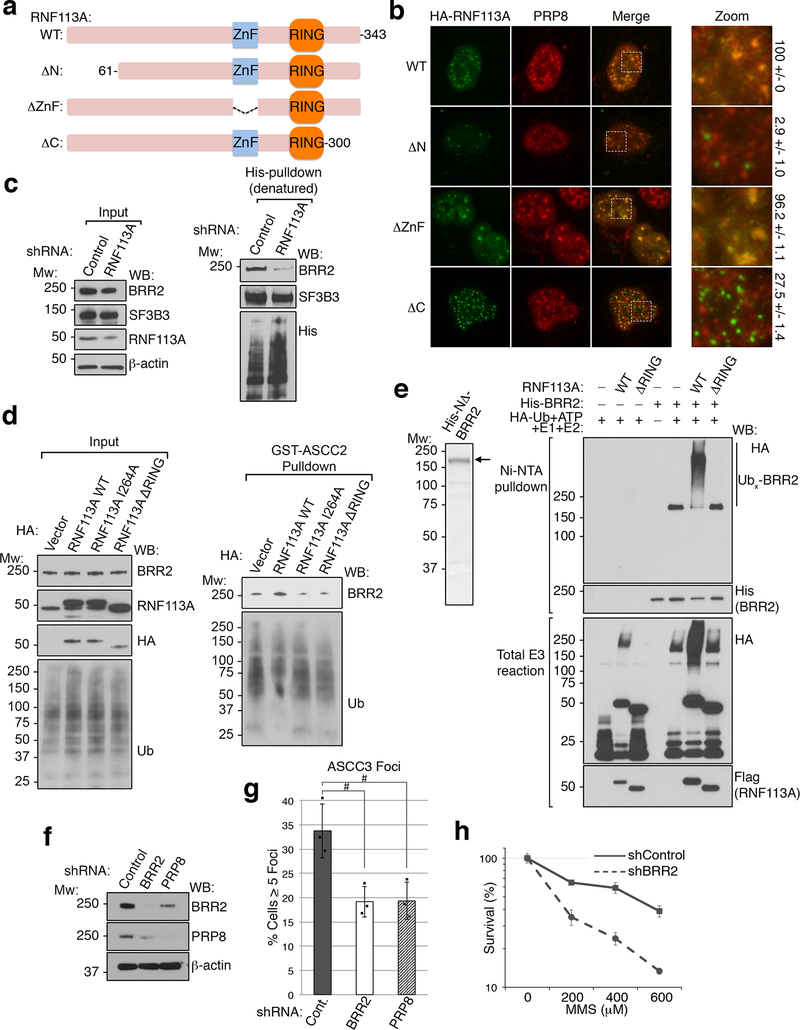
Extended Data Figure 10. Functional characterization of RNF113A.
(a) Schematic of human RNF113A and its domain structure. The three deletion constructs used for localization analysis are also shown. (b) Images of cells expressing WT or the indicated HA-RNF113A deletion constructs. Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantitation of co-localization between each RNF113A construct and PRP8 is shown on the right (n=3 biological replicates; mean ± S.D.). (c) 293T cells expressing His-ubiquitin were transduced with control or RNF113A-targeting shRNAs and treated with MMS. Ubiquitinated proteins were isolated by Ni-NTA under denaturing conditions and Western blotted as shown. Input lysates were also analyzed as indicated. SF3B3, another ubiquitinated spliceosomal protein, was used as a control (n=3 independent experiments). (d) Cells expressing the indicated HA-vectors were treated with MMS as in (c). Lysates were then used for ubiquitin pulldown assays using GST-ASCC2, then blotted as shown. Input lysates were also analyzed as indicated (n=2 independent experiments). (e) His-NΔ-BRR2 was purified from Sf9 cells and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (left). This was then used as a substrate for ubiquitination assays using HA-Ub and wildtype (WT) or a RING-deletion (ΔRING) RNF113A (n=2 independent experiments). (f) Western blot analysis of U2OS cells expressing the indicated shRNAs used for immunofluorescence analysis in Figure 4F (n=2 independent experiments). (g) Quantitation of Figure 4F (n=3 biological replicates; mean ± S.D.; two-tailed t-test, # = p < 0.001). (h) MMS sensitivity of PC-3 cells expressing the indicated shRNAs was determined by MTS assay (n=5 technical replicates; mean ± S.D.).