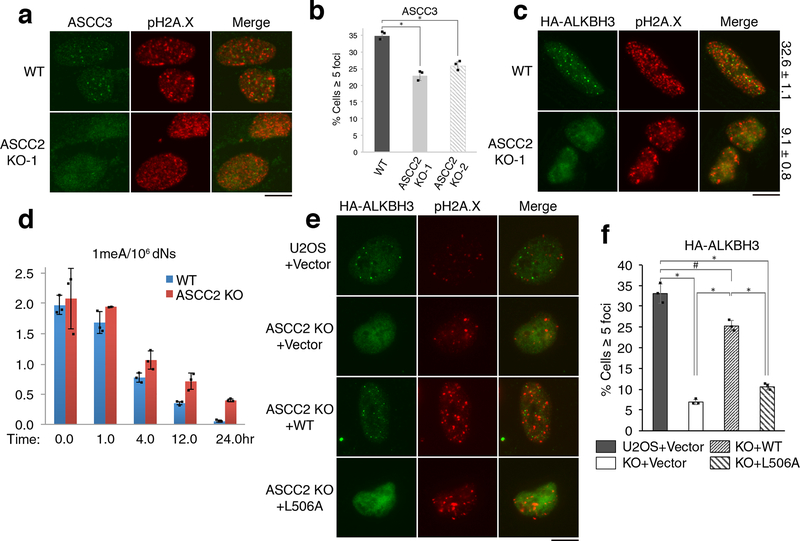
Figure 3. ASCC2 is critical for ASCC3-ALKBH3 recruitment and alkylation resistance.
(a) MMS-induced ASCC3 foci were assessed in WT and ASCC2-KO cells. (b) Quantitation of (a) (n=3 biological replicates; mean ± S.D.; two-tailed t-test, * = p < 0.001). (c) HA-ALKBH3 foci were assessed as in (a). Numbers indicate the percentage of cells expressing five or more foci (n=2 biological replicates; mean). (d) 1meA quantitation in WT or ASCC2-KO cells after MMS treatment (n=3 biological replicates; mean ± S.D.). (e) Images of WT or ASCC2-KO cells expressing indicated vectors upon MMS. (f) Quantitation of (e) (n=3 biological replicates; mean ± S.D.; two-tailed t-test, * = p < 0.001, # = p < 0.05). Scale bars, 10 μm.