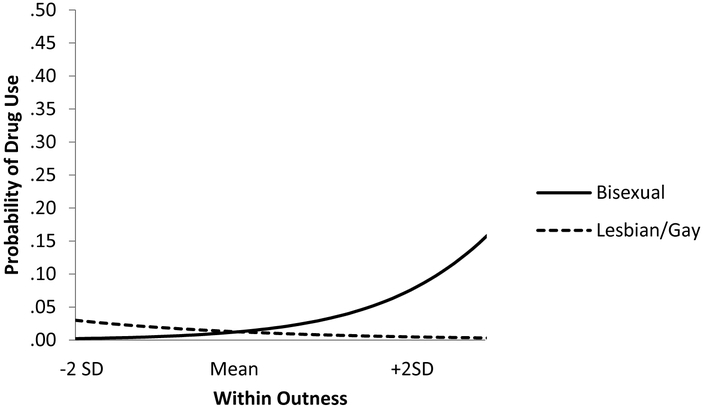
Figure 3.
Association between outness and change in illicit drug use as a function of sexual identity. Being more out was associated with increases in the odds of illicit drug use for bisexuals (b = 1.68, SE = .42, z = 4.00, p < .001, OR = 5.36) and with decreases for gay/lesbian individuals (b = −.85, SE = .43, z = −1.99, p = .046, OR = .43). Expected probability of illicit drug use is calculated holding all covariates at their means.