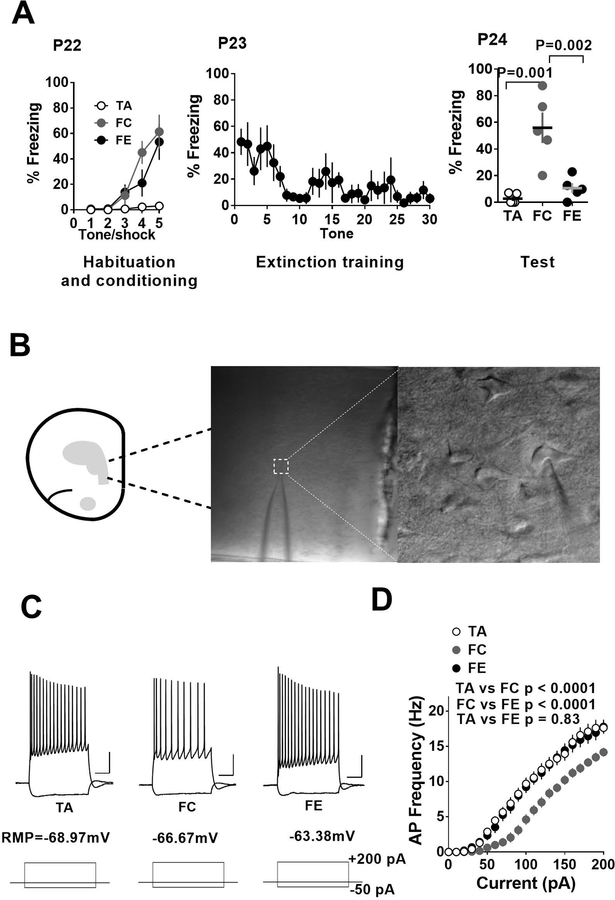
Figure 1.
Fear conditioning and extinction result in a bidirectional modulation of excitability in IL-mPFC layer 5 pyramidal neurons of pre-adolescent mice. A) Average freezing during exposure to tone alone or tone-shock pairing on day 1, during extinction training on day 2 and fear memory test on day 3. B) Schematic presentation and an example of whole cell recording in IL-mPFC layer 5 pyramidal neurons. C) Example traces of voltage responses to hyperpolarizing (−50 pA) and depolarizing (+200 pA) current steps in pyramidal neurons from tone alone (TA), fear condition (FC) and fear extinction (FE) groups. Scale: 250 ms/20 mV. D) Current vs. action potential (AP) frequency plot in tone alone (16 neurons/5 mice), fear condition (18 neurons/5 mice) and fear extinction (19 neurons/5 mice) groups. The fear condition group showed fewer action potentials compared to tone alone group and this effect was reversed by fear extinction.