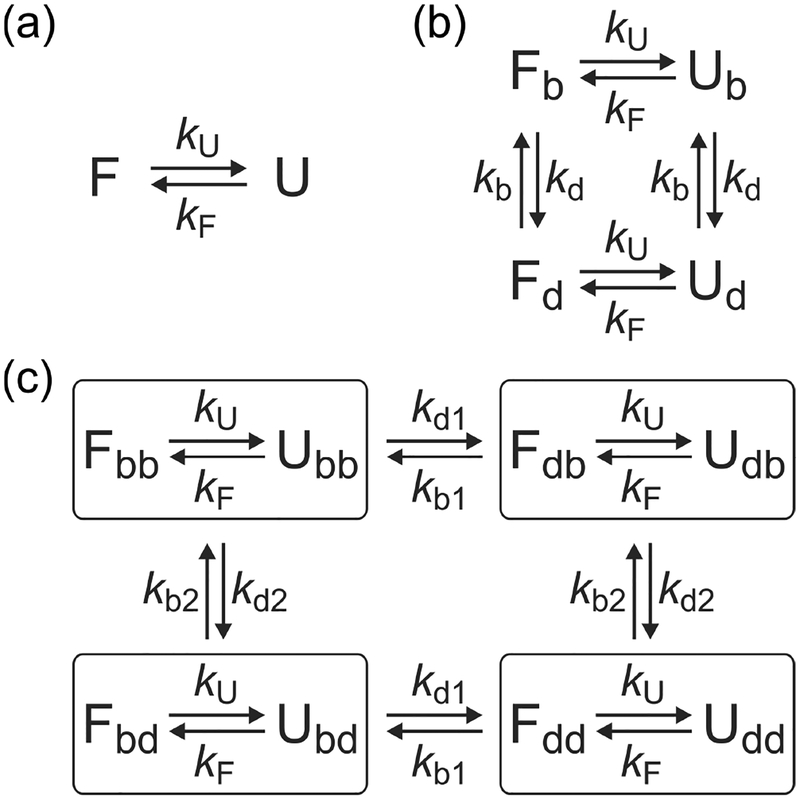
Figure 3.
Kinetic models used in the maximum likelihood analysis. (a) Two-state model consisting of the folded (F) and unfolded (U) states with folding and unfolding rate coefficients kF and kU. (b) Four-state model to account for blinking of acceptor. kb (kd) is the rate coefficient from the bright (dark) to the dark (bright) state of the acceptor. (c) Eight-state model including blinking of acceptor 1 and acceptor 2. kbI (kdI) is the rate coefficient from the bright (dark) to the dark (bright) state of acceptor I. Note that acceptor blinking occurs between the folded states and between the unfolded states, but not between the folded and unfolded states with different acceptor states similar to the blinking transitions in (b).