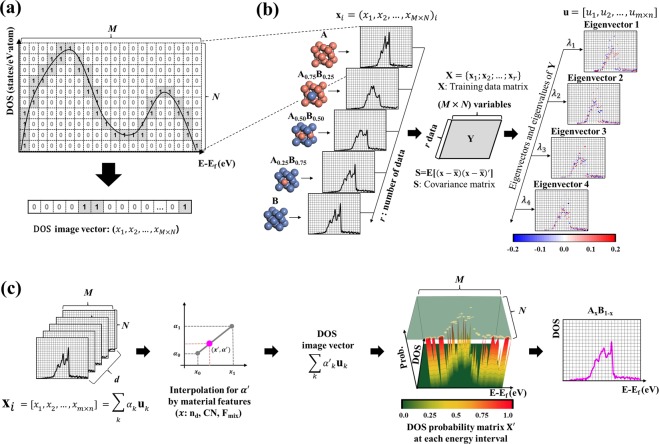
Figure 1.
Scheme of the pattern learning (PL) method for learning and predicting electronic DOSs. (a) Conversion of a DOS pattern from a continuous energy function in a rectangular window to a digital image vector with M × N entries. (b) Learning process of PCs of AxB1−x alloys with their DOS patterns. xi is a row vector where M and N correspond to the grid size of the DOS window, and is the average value of the entries in the row vectors. As a training system for learning, five compositions (A, A0.75B0.25, A0.50B0.50, A0.25B0.75, and B) are considered on the left side. A covariance matrix, Y, is constructed in the middle. PCA determine the eigenvectors, which are PCs, and eigenvalues of the training data set, which are shown on the right side. (c) The prediction process of an unknown DOS pattern for an arbitrary alloy, AxB1-x. The process involves several steps: (1) estimation of PC coefficients using features, including nd, CN, and Fmix; (2) estimation of a new DOS image vector; (3) production and utilization of the DOS probability matrix; and (4) prediction of the DOS pattern for the test alloy, AxB1-x, using a probability matrix.