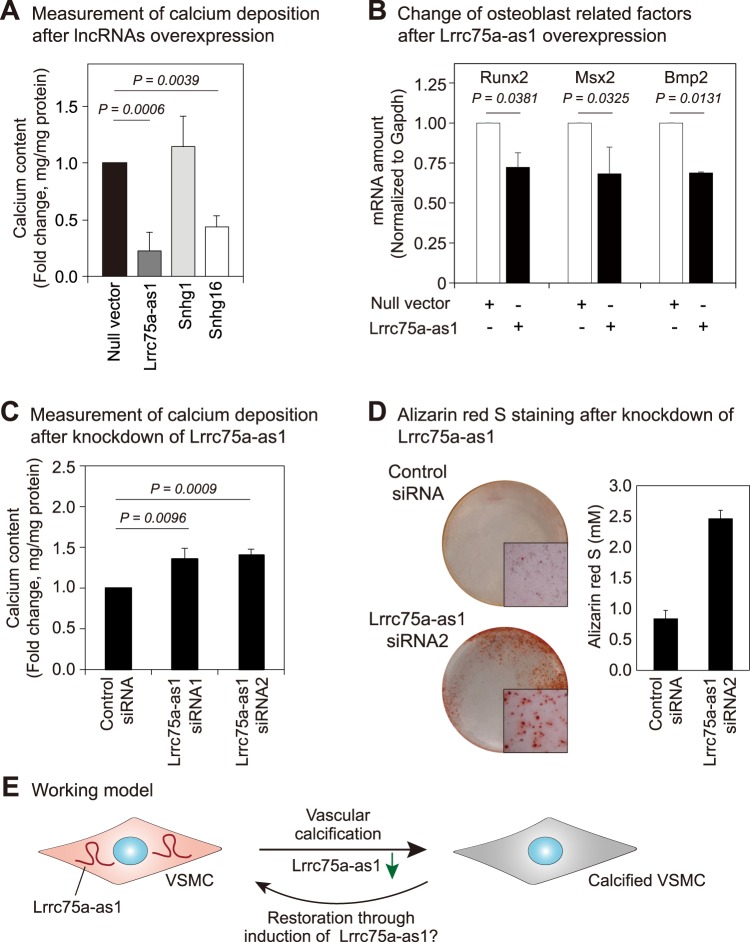
Figure 4.
Lrrc75a-as1 inhibits vascular calcification. (A) Measurement of calcium deposition after overexpression of candidate lncRNAs. Compared to other lncRNAs, overexpression of Lrrc75a-as1 most significantly changed the calcium content. Error bars indicate standard error between four independent experiments with triplicates in each experiment. P value was calculated by a two-sided paired t-test. (B) Expression change of the osteoblast-related factors after Lrrc75a-as1 overexpression. The expression of osteoblast-related factors, including Runx2, Msx2, and Bmp2 was measured. Error bars indicate standard error between three independent experiments. (C) Measurement of calcium deposition after knockdown of Lrrc75a-as1. Six independent experiments were performed, and the P value was calculated by a two-sided paired t-test. (D) Determination of calcification with Alizarin red S staining. After the knockdown of Lrrc75a-as1, the calcium deposits were measured with Alizarin red S dye. The pictures of cell culture dishes and microscopic images (50×) were shown. The amounts of Alizarin red S-stained mineralization were quantified from three cell culture dishes and error bars indicate the standard errors. (E) Working model. The expression level of Lrrc75a-as1 is reduced during vascular calcification in VSMCs. Upregulation of Lrrc75a-as1 expression may switch the VSMC phenotype from an osteoblastic/chondrogenic to a contractile phenotype, and mitigate calcium accumulation.