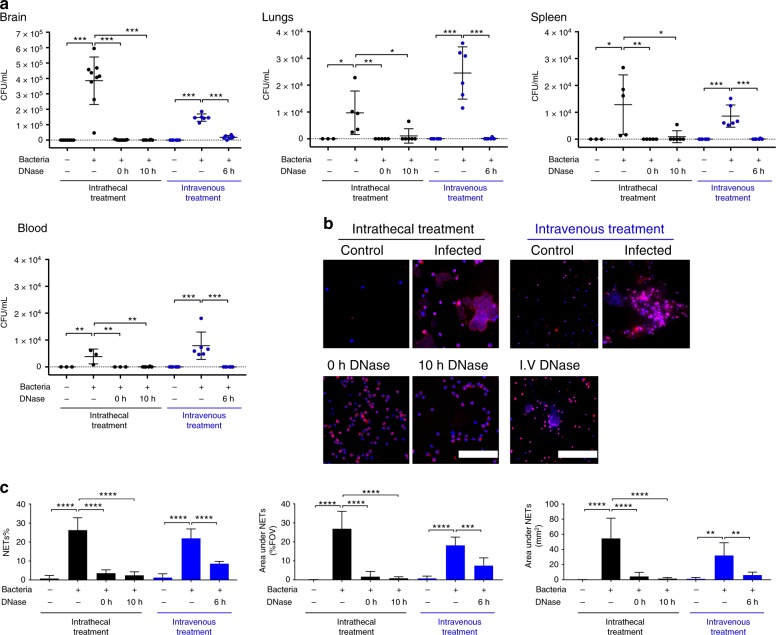
Fig. 4.
DNase facilitates bacterial clearance in a rat model of pneumococcal meningitis. Rats received a subarachnoid infusion of either S. pneumoniae SP001 strain (infected) or equal volume of saline solution (control). a After the rats were sacrificed, the brain, the right lung, and the spleen were collected and homogenized immediately. The blood was collected and centrifuged to obtain plasma. Organ homogenates and blood plasma samples were spread onto agar plates and resulting bacterial colonies were counted after 24 h. Indicated groups were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 and error bars denote standard deviations. b To determine the effect of intrathecal DNase treatment, infected rats either received a subarachnoid infusion of 10 units of DNase simultaneously (0 h) or 10 h after the infection, or they received an equal volume of saline vehicle solution simultaneously to the infection. To determine the effect of intravenous DNase treatment, infected rats either received an intravenous bolus dose of 3500 units of DNase 6 h after the infection, followed by intravenous infusion of 780 units/h over the next 18 h, or they received an equal volume of saline vehicle control in the same manner. In all cases, uninfected (control) rats received an equal volume of saline vehicle control either intrathecally or intravenously as indicated. All rats were sacrificed 24 h after the infection. Cerebrospinal fluid was collected for visualization of NETs only by immunofluorescence against rat myeloperoxidase (red) and DNA (blue). Areas of red and blue colocalization represent NETs. Scale bars denote 200 µm. c NETs were quantified using Fiji and expressed as percentage of NETs, percentage of staining under NETs per field of view and total area under NET staining in square millimeters. Indicated groups were compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, centre line and columns indicate mean values **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001 and error bars denote standard deviations