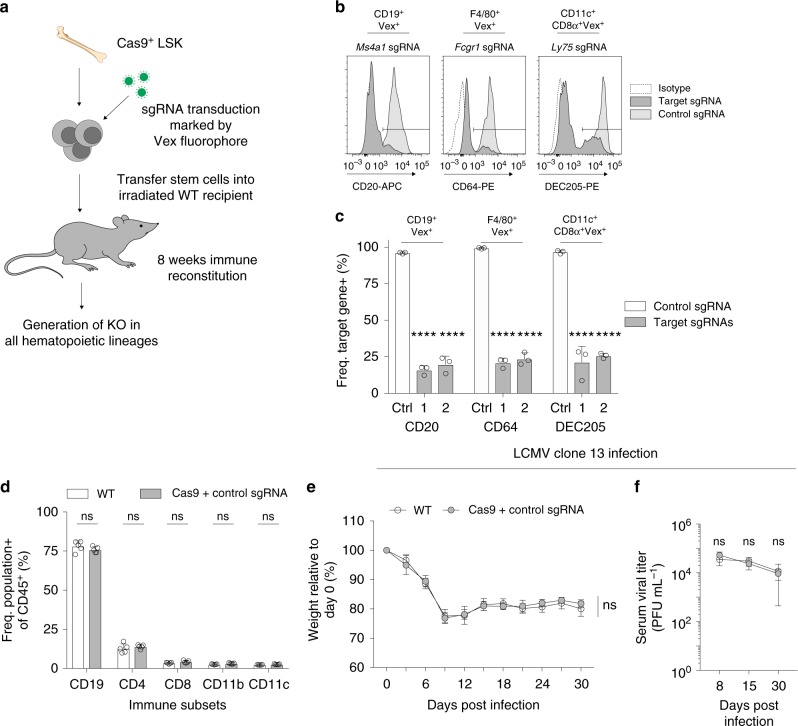
Fig. 1.
CHIME enables deletion of genes without impairing immune homeostasis. a Schematic of chimeric CRISPR-Cas9 system. b CD20 (left), CD64 (middle), or DEC205 (right) expression on B cells, macrophages, or dendritic cells, respectively from chimeric animals following transduction with a non-targeting control sgRNA or targeting sgRNAs to Ms4a1, Fcgr1, or Ly75. c Quantification of CD20, CD64, and DEC205 expression on relevant lineages from (b). d Comparison of frequencies of major immune lineages (of CD45+) in chimera mice (WT: WT stem cells mock transduced, Cas9 + sgRNA: Cas9 stem cells transduced with the Vex sgRNA expression vector) at homeostasis. e, f Chimeric mice were infected with 4 × 106 plaque-forming units (PFU) LCMV Clone 13 and their weight loss (e) and serum viral titer (f) were determined. All experiments had at least three biological replicate animals per group and are representative of two independent experiments. Bar graphs represent mean and error bars represent standard deviation. Statistical significance was assessed among the replicate bone marrow chimeras by one-way ANOVA (c, d), or two-way ANOVA (e, f) (*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001). See also Supplementary Fig. 1 and 2. Source data are provided as a source data file