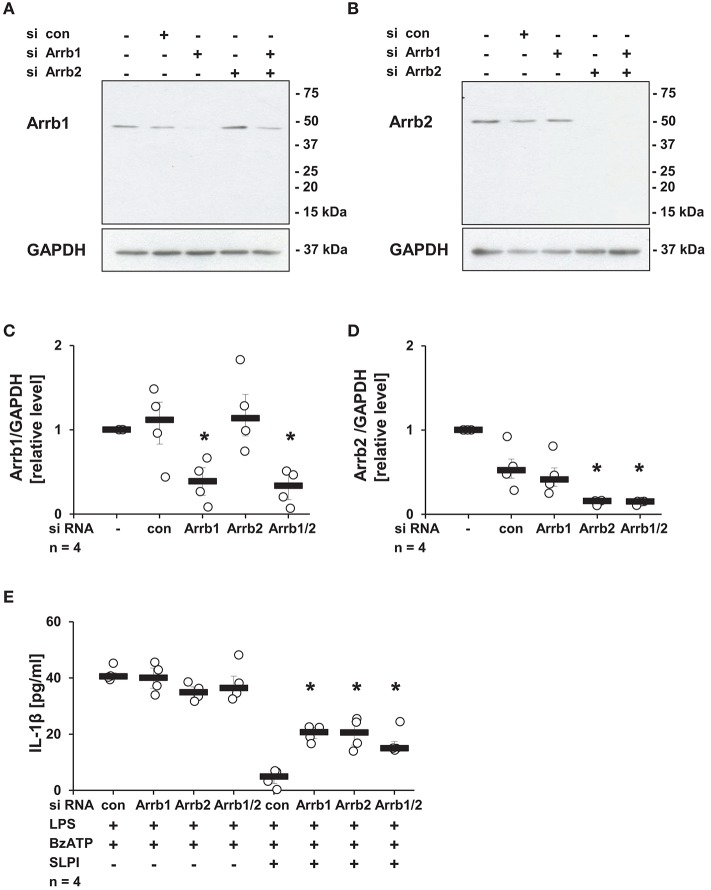
Figure 9.
SLPI signaling involves arrestin β1 and 2 (Arrb1/2). Expression of Arrb1 or Arrb2 in U937 cells was diminished using siRNA. Afterwards, cells were primed with LPS (1 μg/ml, for 5 h) and further stimulated with 2′(3′)-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine 5′-triphosphate triethylammonium salt (BzATP; 100 mM) for 30 min in the presence or absence of SLPI (10 μg/ml). The efficiency and specificity of the knock-down was confirmed by immunoblotting. The concentration of IL-1β in cell culture supernatants was measured by ELISA. (A,C) The expression level of Arrb1 was selectively lowered upon transfection with Arrb1 siRNA; (A) representative immunoblot out of 4 (B,D) The expression level of Arrb2 was diminished upon transfection with Arrb2 siRNA; (B) representative immunoblot out of 4. (C,D) Optical density of the immune-positive bands for Arrb1 or Arrb2 was measured and divided by the values obtained for β-actin on the same blot. The values gathered from untreated cells were set to one and all other values were calculated accordingly. *p ≤ 0.05 significantly different compared to cells transfected with control (con) siRNA. (E) Down-regulation of the expression of Arrb1 or Arrb2 by siRNA blunted the SLPI-induced inhibitory effect. *p ≤ 0.05 significantly different compared to cells transfected with control siRNA (con) and stimulated with LPS, BzATP and SLPI. Experimental groups were compared by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann-Whitney rank sum test.