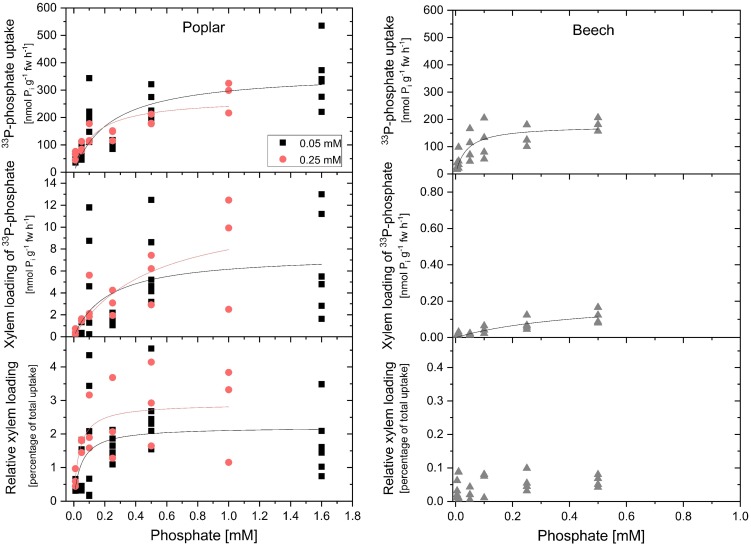
FIGURE 2.
Concentration dependency of phosphate uptake, xylem loading of phosphate and the relative proportion of phosphate loaded into the xylem of excised poplar and beech roots. Concentration dependency of phosphate (Pi) uptake (upper graphs), xylem loading of phosphate (middle graphs) and the relative proportion of phosphate loaded into the xylem (bottom graphs) was performed with excised poplar (left column) and beech (right column) roots. Poplar plants were grown either with 0.05 mM Pi (black squares) or with 0.25 mM Pi (red dots). Beech seedlings were cultivated with 0.02 mM Pi. Data presented are values from individual incubations with four to six excised roots. Michaelis–Menten fits were calculated using the data analysis and graphic software Origin®9.1. The black and red curves show Michaelis–Menten fits for the respective plant sets; black: growth Pi = 0.05 mM; red: growth Pi = 0.25 mM for poplar, and gray for beech. After 2 h of pre-incubation the 4 h of incubation were started by replacing the solution of the incubation compartment with the respective incubation solution containing the Pi concentration indicated; for poplar from 0.01 mM up to 1.6 mM Pi and for beech from 5 μM up to 0.5 mM Pi. Specific activity of 33P-Pi ranged from ∼2.0∗108 Bq mmol-1 (application of 0.05 mM Pi) up to ∼5.7∗106 Bq mmol-1 (treatment of 1.6 mM Pi) for poplar and ranged from ∼1.9∗109 Bq mmol-1 (application of 0.005 mM Pi) up to ∼1.9∗107 Bq mmol-1 (treatment of 0.5 mM Pi) for excised beech roots.