Figure 5.
The Exonuclease XRN1 in Cells Infected with SINV
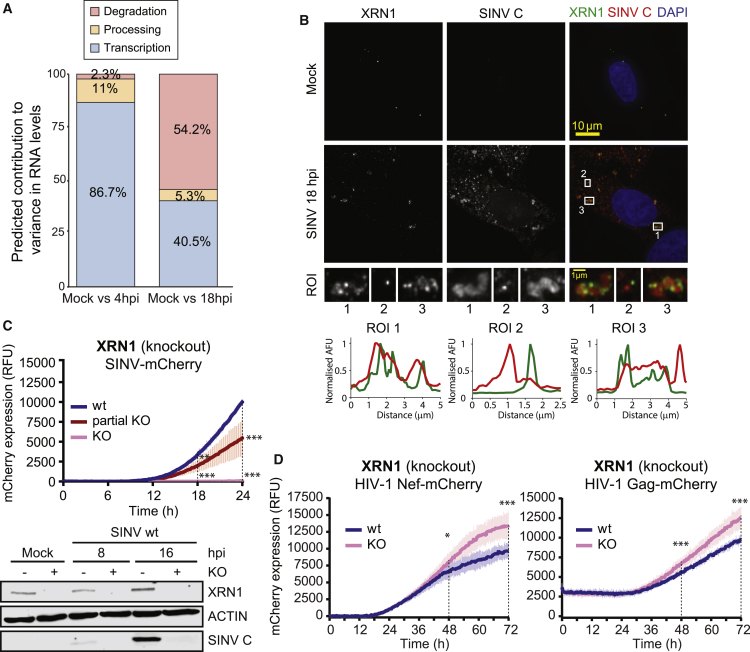
(A) Contribution of transcription, processing, and degradation to the transcriptomic changes induced by SINV. We compared our RNA-seq data to available data estimating these parameters (Mukherjee et al., 2017). ANOVA was used to predict the contribution of each RNA biological process to the variance in RNA levels.
(B) Immunolocalization of XRN1 and SINV C. Green and red fluorescence profiles for regions of interest (ROI) are displayed.
(C) Top: mCherry fluorescence in XRN1 KO and control cells infected with SINV-mCherry measured every 15 min in a plate reader with atmospheric control (5% CO2 and 37°C). RFU, relative fluorescence units. Western blot of XRN1 and SINV C (bottom).
(D) Infection fitness of HIV-1Nef-mCherry and HIV-1Gag-mCherry pseudotyped viruses in XRN1 KO cells. mCherry expression was measured as in (C).
mCherry fluorescence is represented as mean ± SD of three independent infections in each of the three biological replicates (n = 9). ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05.
See also Figure S5.