Figure 7.
Effects of RBPs with Antiviral Potential in SINV Infection
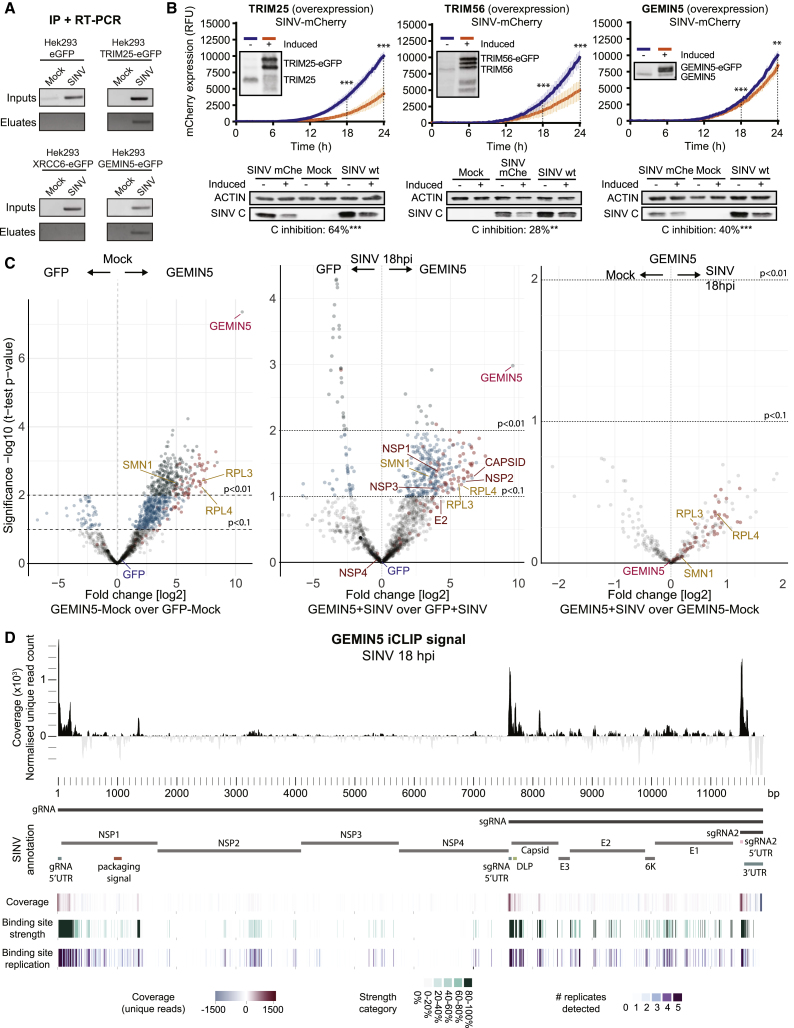
(A) UV crosslinking and immunoprecipitation of TRIM25-EGFP, GEMIN5-EGFP, XRCC6-EGFP, or unfused EGFP in cells infected or not with SINV for 18 h. The presence of SINV RNA in eluates and inputs was detected by RT-PCR using specific primers against SINV RNAs.
(B) Relative mCherry fluorescence produced in cells overexpressing TRIM25-EGFP (top left), TRIM56-eGFP (top middle), GEMIN5-eGFP (top right), and infected with SINV-mCherry (measured as in Figure 5C). mCherry expression is represented as the mean ± SD of three independent infections in each of the three biological replicates (n = 9). Overexpression was assessed by western blotting. Bottom: western blots of SINV C at 18 hpi, indicating below the average inhibition of C relative to control cells. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p < 0.01.
(C) Volcano plots comparing the intensity of proteins in GEMIN5-EGFP versus unfused EGFP IPs in uninfected (left) and infected cells (middle); every dot represents a protein. Dark green dots are proteins enriched with p < 0.01, blue dots are those enriched with p < 0.1, and gray dots represent nonenriched proteins. Pink dots represent ribosomal proteins. Right: a volcano plot comparing the intensity of proteins in GEMIN5 IPs in infected versus uninfected cells.
(D) iCLIP analysis of GEMIN5-binding sites on SINV RNA. Top: coverage pileup of 5′ first base of unique molecules mapping to the SINV genome, shown as 20-nt sliding mean of five replicates after GFP background subtraction. Each position is given relative to total SINV count (RPM). Middle: key features of SINV annotation. Bottom: the top track shows iCLIP coverage but as a heatmap representation. The middle heatmap shows GEMIN5 binding sites along SINV divided into five groups according to strength of binding. The bottom heatmap shows the number of replicates supporting each binding site when binding sites are called independently for each replicate.