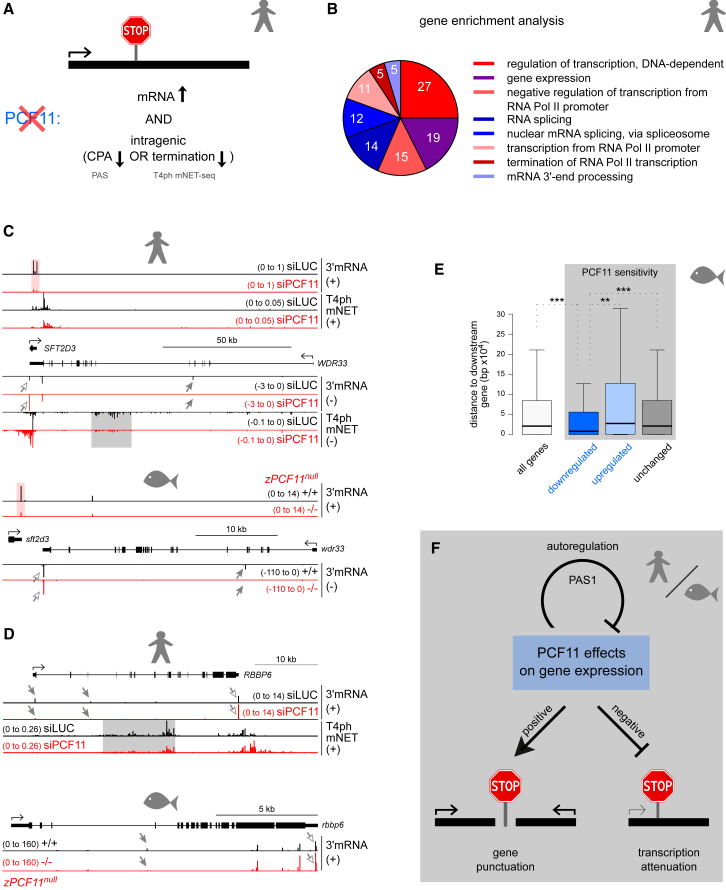
Figure 7.
Transcriptional Regulators Are Controlled by PCF11-Dependent Premature CPA and Termination
(A) Criteria for identifying genes attenuated by PCF11-dependent premature CPA/termination: these are significantly upregulated upon PCF11 depletion (DEseq padj < 0.05) and either show a >2-fold decreased intragenic T4ph mNET-seq signal or possess a significantly decreased PAS (DEXseq padj < 0.1).
(B) Enrichment analysis of GO biological process for transcripts attenuated by PCF11 in human cells. Numbers in pie chart correspond to number of genes in each category. GeneCodis3 software was used (padj < 0.01 and gene number >2). Red shades, genes related to transcription; blue shades, genes related to RNA processing.
(C and D) Genomic profiles ± PCF11 of WDR33 (C) and RBBBP6 (D) for human cells (top) and zebrafish embryos (zPCF11null, bottom). Gray shading highlights decreased intragenic T4ph mNET-seq signal, and arrows highlights distal APA in PCF11-depleted conditions (gray arrowheads: decreased intragenic PAS signal, white arrowheads: increased 3′ UTR PAS usage).
(E) Gene distance analysis for genes significantly downregulated, upregulated or unchanged in zPCF11null−/− versus +/+ embryos. Statistical significance was tested by Mann-Whitney test.
(F) Model: PCF11 displays opposing functions in gene expression. PCF11 punctuates closely spaced genes, leading to their gene expression enhancement. In contrast, PCF11 negatively affects the expression of a subset of transcriptional regulators by attenuating their transcription. PCF11 is also autoregulated by PAS1-dependent premature CPA and termination.