Figure 3.
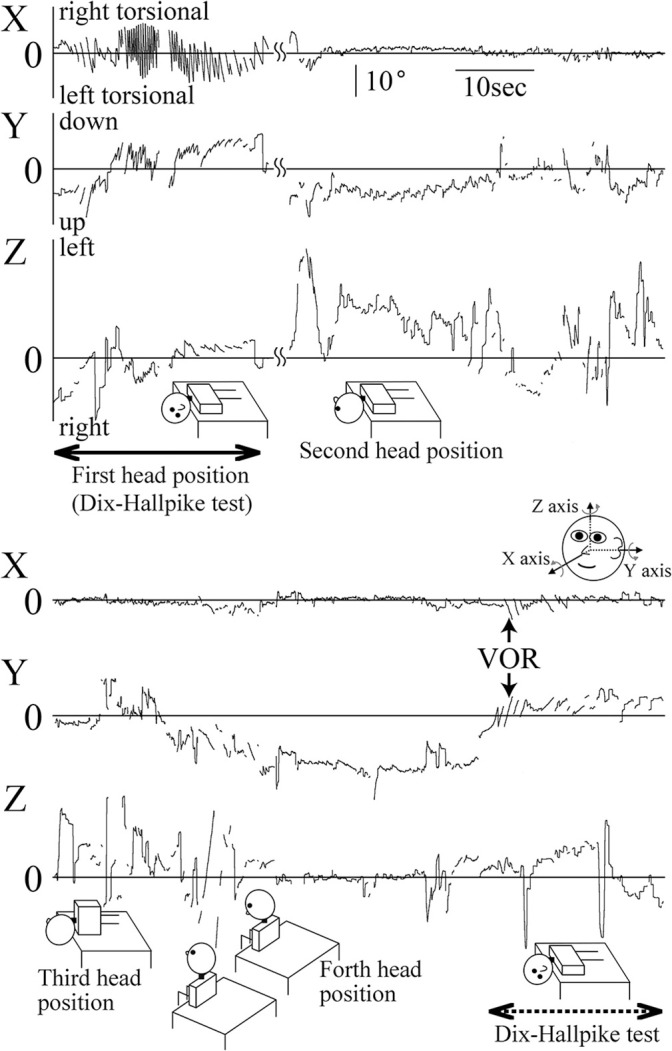
Three-dimensional axis angles of eye position of a representative patient who was allocated to group A during the Epley maneuver (EM) and the following Dix-Hallpike test. Highest column: X component (torsional component), middle column: Y component (vertical component), lowest column: Z component (horizontal) component. Because this figure contains data that were recorded during the head movement of EM, positional nystagmus and nystagmus induced by vestibulo-ocular reflex during the head movement could be observed. At the part indicated by a solid double headed arrow, the head was at that position where we observed positional nystagmus induced by the first right Dix-Hallpike test. From this head position, next, the head was moved to the second head position of the EM. Therefore, this head position is also the first head position of the EM. At this part, very strong positional nystagmus could be seen, especially in X and Y components. The positional nystagmus was right torsional and upward attenuated nystagmus. This positional nystagmus was typical of nystagmus seen in patients with right side-affected posterior canal type of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (13). At the second head position, very weak downward nystagmus could be seen (Y component). At the third head position, no clear nystagmus could be seen. At the fourth head position, very weak downward nystagmus could be seen (Y component). At the following second right Dix-Hallpike test, the part was shown by dotted double head arrows, very weak right torsional and upward positional nystagmus could be seen. Note that a positive Y component indicates downward rotation, while a negative Y component indicates upward rotation; a positive Z component indicates leftward rotation, while a negative Z component indicates rightward rotation.
