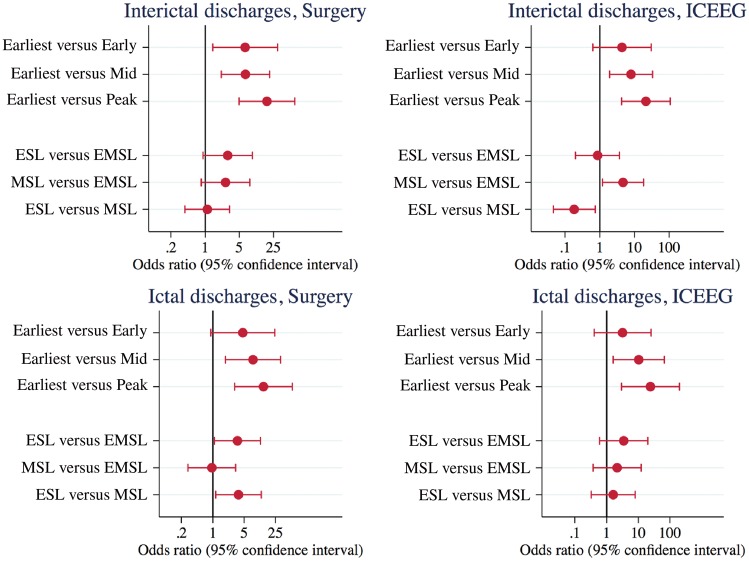
Figure 2.
Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for source solution agreement with epileptogenic zone as defined by intracranial EEG and surgical resection margins. By phase, the results indicate better epileptogenic zone agreement for earliest (as first modality early-phase solution/s) against early-phase (ictal-SU) solutions, and against all corresponding mid-phase (as 50% mean global field power or 50% upstroke phase discharge, whichever first) and late-phase (negative peak) solutions. By method, epileptogenic zone agreement was better for ESL versus EMSL and for ESL versus MSL for ictal-SU, while epileptogenic zone agreement was better for MSL versus EMSL and for MSL versus ESL for IED-ICEEG. This indicates a superiority of independent ESL plus MSL over either method alone and over combined EMSL for non-invasive epileptogenic zone characterization. EZ = epileptogenic zone; SU = surgical resection margins.