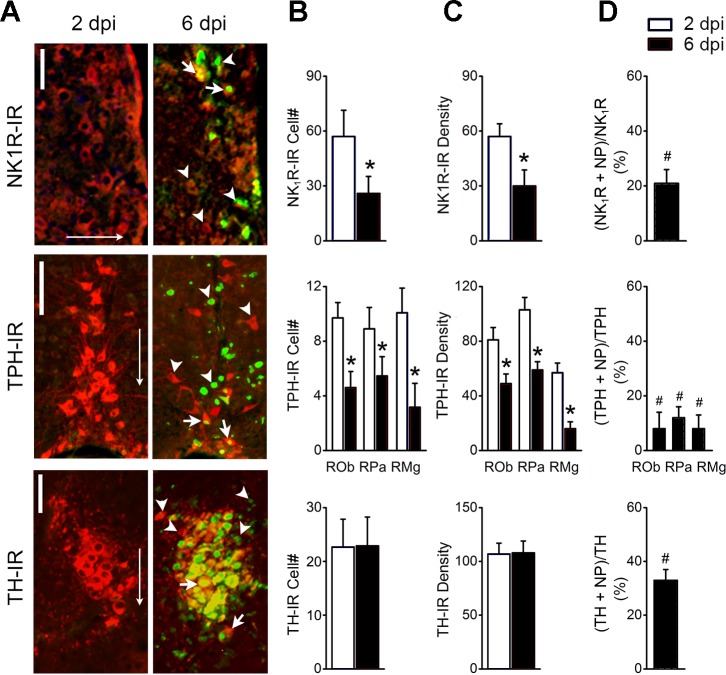
Fig. 5.
Double labeling of nucleoprotein immunoreactivity (NP-IR), with the neurons expressing neurokinin 1 receptor immunoreactivity (NK1R-IR) in the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN), tryptophan hydroxylase immunoreactivity(TPH-IR) in the medullary raphe (ROb, RPa, and RMg nuclei), and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity (TH-IR) in the locus coeruleus (LC) at 2 and 6 postinfection (dpi); n = 5. A: typical micrographs showing nucleoprotein (NP) co-labeled with NK1R-IR in the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN; top), TPH-IR in the medullary raphe (ROb, RPa, and RMg nuclei; middle), and TH-IR in the LC (bottom) at 6 but not 2 dpi. Arrowheads indicate single labeling of NP (green) or NK1R/TPH/TH-IR alone (red), and arrows indicate the co-labeling of NP-IR with the cell marker NK1R-, TPH-, or TH-IR. Scale bars, 50 µm. Arrows point toward ventral. B: %double-labeled neurons relative to the single-labeled neurons in the corresponding nucleus. C: averaged neuronal populations double labeled with NP + NK1R-IR in the RTN, NP + TPH-IR in the raphe, and NP + TH-IR in the LC at 2 and 6 dpi. D: averaged grayscale values of neurons expressing NK1R-IR in the RTN, TPH-IR in the medullary raphe, and TH-IR in the LC. #P < 0.05 compared with NK1R-, TH- or TPH-IR neurons without NP-IR couple-labeling (“0”); *P < 0.05 compared with 2 dpi.