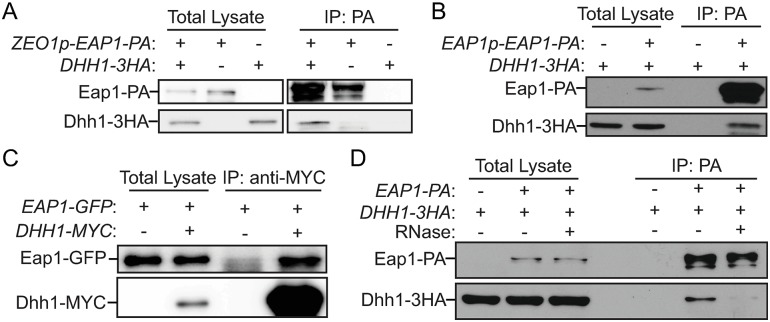
Fig 5. Dhh1 interacts with Eap1 under nitrogen-starvation conditions.
(A) ZEO1p–EAP1–PA (ZYY207; ZEO1p), DHH1–3HA (ZYY208), and ZEO1p–EAP1–PA DHH1–3HA (ZYY209) cells were grown in YPD to mid-log phase (-N, 0 h) and then shifted to SD-N for 2 h. The samples were collected and subjected to the protein–protein IP procedures described in the Materials and methods. The analysis of the samples by western blot is shown. (B-D) Cells were cultured and subjected to procedures as indicated in (A). The analysis of the samples by western blot is shown: (B) DHH1–3HA (ZYY208) and DHH1–3HA EAP1p–EAP1–PA (XLY345; EAP1 promoter); (C) ZEO1p–EAP1–GFP (XLY346) and DHH1–MYC ZEO1p–EAP1–GFP (YZY256); (D) DHH1–3HA (ZYY208) and ZEO1p–EAP1–PA DHH1–3HA (ZYY209). The RNase treatment during incubation with IgG beads was conducted as described in the Materials and methods. (See also S6 Fig). Eap1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E–associated protein 1; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitation; PA, protein A; SD-N, synthetic minimal medium lacking nitrogen; YPD, yeast extract–peptone–dextrose; ZEO1p, zeocin resistance 1 promoter.