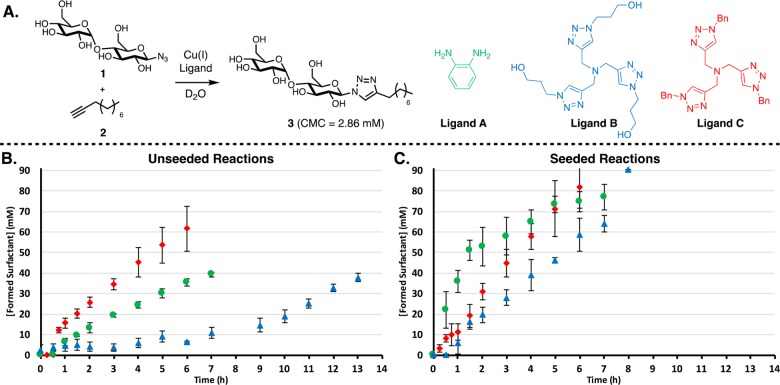
Figure 2.
(A) Reactions where maltose azide 1 is coupled to alkyne 2 via a CuAAC reaction to form surfactant 3 and the structures of ligands used. Ligands A and B are hydrophilic, and ligand C is hydrophobic. (B) Kinetic results showing the influence of the ligand; A (green circles), B (blue triangles), and C (red diamonds), on the rate of conversion. A trend is observed where increased hydrophobicity of the ligand results in higher rates of conversion. (C) When seeding reactions with 22 mM of product, elimination of the lag period and higher reaction rates are observed. The reaction is monitored by consumption of azide 1 and formation of surfactant 3 by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Points are the mean of three independent experiments, and the error bars are the standard deviation.