Fig. 1.
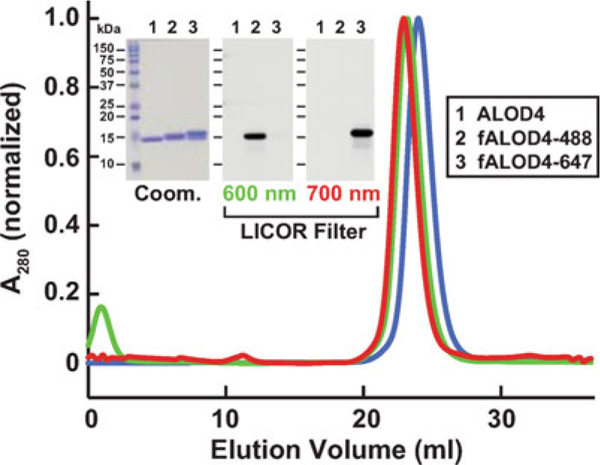
Biochemical characterization of ALOD4. Gel filtration chromatography of purified proteins. Recombinant ALOD4 was purified and labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (fALOD4-488) or Alexa Fluor 647 (fALOD4-647) fluorescent dyes as described in Subheading 3. Buffer B (1 mL) containing 0.8 mg of ALOD4, fALOD4-488, or fALOD4-647 was loaded onto a Tricorn 10/300 Superdex 200 column and chromatographed at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. Absorbance at 280 nm (A280) was monitored continuously to identify ALOD4(blue), fALOD4-488(green), or fALOD4-647(red) proteins. Maximum A280 values for each protein (ALOD4: 390 mAU, fALOD4-488: 231 mAU, and fALOD4-647: 279 mAU) are normalized to 1. (Inset) 3 μg of each protein was subjected to 15% SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie (left) or imaged with the 600 nm filter (middle) or the 700 nm filter (right) on a LICOR instrument. Coom, Coomassie. Figure adapted from [7]
