Figure 5. Summarizes the major classes of cholesterol-dependent anti-Mtb compounds identified in a screen against intracellular Mtb.
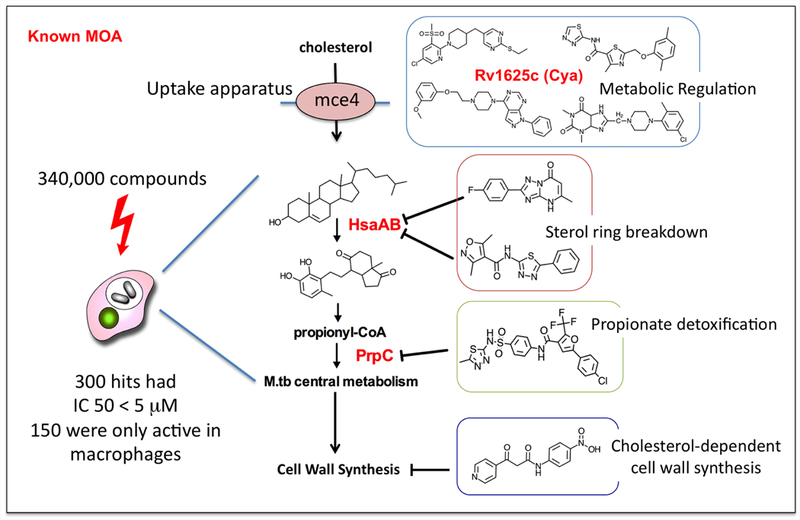
The primary screen of 340,000 compounds identified 300 hits with IC 50 of less than 5μM, 50 % of which only showed activity against intracellular bacteria and had no activity against Mtb in rich broth. However, the majority of these compounds recovered their activity when Mtb was grown in medium with cholesterol or fatty acids as the limiting carbon source. This figure summarizes the major targets or functions inhibited by the compounds. Activators of an adenylate cyclase (rv1625c, Cya) were shown to be involved in regulation of cholesterol utilization, as well as specific inhibitors of enzymes, HsaAB and PrpC, involved in cholesterol breakdown or propionyl-CoA detoxification. Data taken from VanderVen et al. (70).
