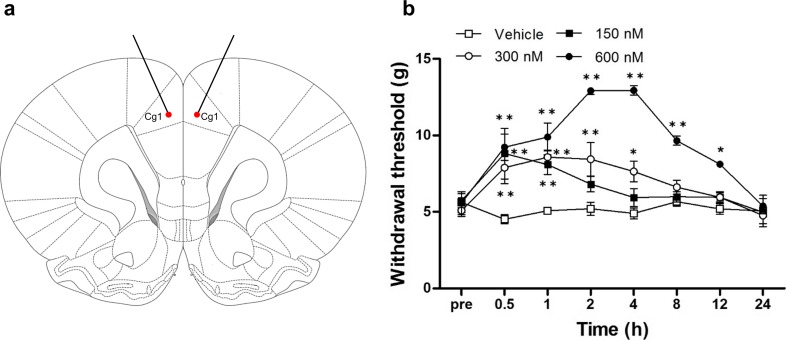
Fig. 3.
Microinjection of rapamycin into the ACC attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity. a Stereotaxic location of rapamycin microinjection into the ACC. Red dots point at microinjection sites and Cg1 indicates cingulate cortex, area 1 in the rat brain atlas. Stainless steel guide cannulae for drug microinjection were bilaterally implanted into the ACC. b Changes in paw withdrawal threshold to mechanical stimulation after microinjection of rapamycin or vehicle on POD 7. Significant differences in withdrawal threshold between 150 nM rapamycin and vehicle groups were observed between 0.5 and 1 h after microinjection. Withdrawal thresholds in the 300 nM rapamycin group were significantly elevated between 0.5 and 4 h after microinjection. The most pronounced changes in withdrawal threshold were observed in the 600 nM rapamycin group, with significant changes observed between 0.5 and 8 h after microinjection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle, two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test