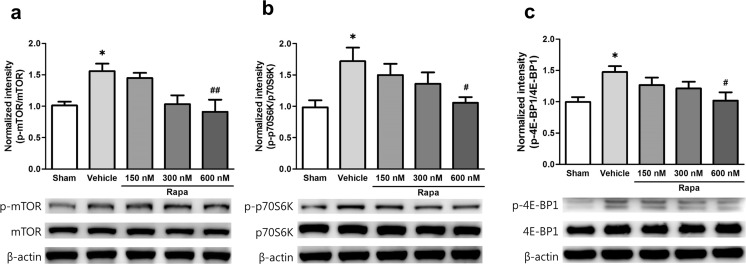
Fig. 4.
Microinjection of rapamycin into the ACC suppresses activation of mTOR and its downstream effectors after nerve injury. a–c Expression of p-mTOR, p-p70S6K, and p-4E-BP1 after microinjection of rapamycin. Levels of p-mTOR, p-p70S6K, and p-4E-BP1 were significantly increased in the vehicle group compared with the Sham group and significantly decreased in all rapamycin groups (Rapa) compared with the vehicle group in a dose-dependent manner. Levels of p-mTOR, p-p70S6K, and p-4E-BP1 were most prominently reduced in the 600 nM rapamycin group compared with the vehicle group. Total protein levels were similar among groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. Sham; #p < 0.05 vs. vehicle, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test