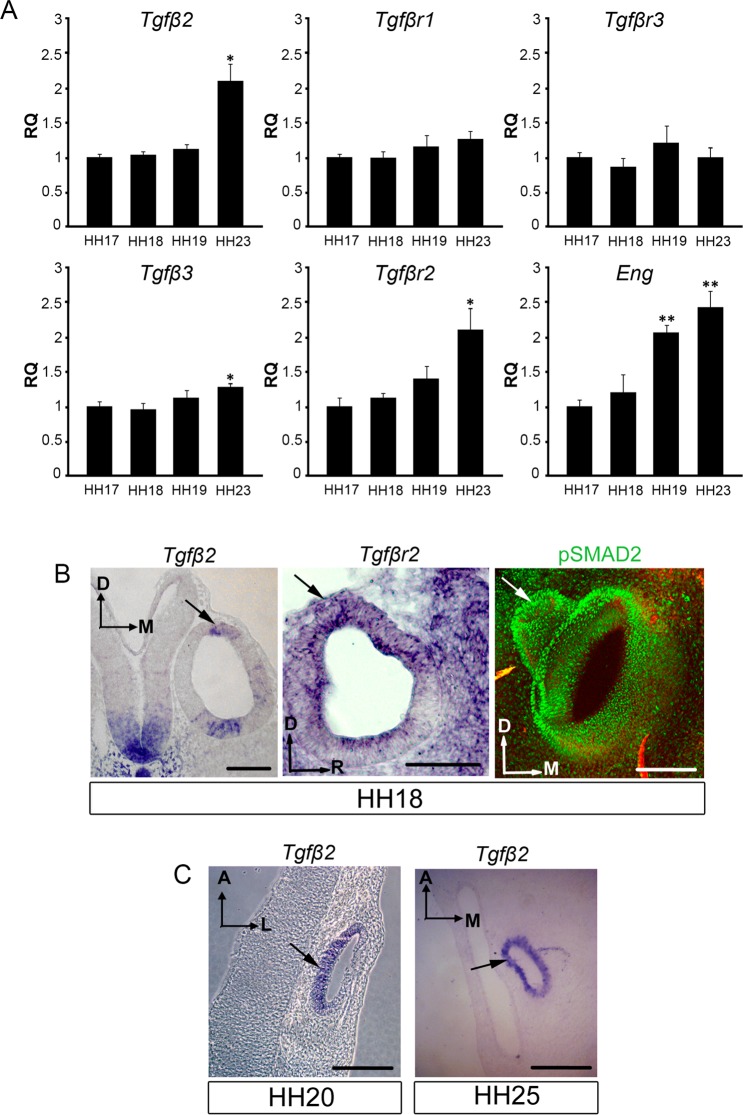
Figure 3.
TGFβ pathway expression in the inner ear during early development. (A) Expression of Tgfβ2, Tgfβ3, Tgfβr1, Tgfβr2, Tgfβr3 and Eng mRNA in the inner ear was measured by RT-qPCR at the indicated developmental stages. Eukaryotic 18s rRNA was used as an endogenous control gene. Gene expression was calculated as 2−ΔΔCt and normalized to the HH17 levels. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM from four independent experiments. (B) TGFβ pathway components (Tgfβ2, Tgfβr2 and pSMAD2) expression in inner ear sections. At HH18 Tgfβ2 was expressed in the dorsal area of the otic epithelium, where the endolymphatic duct will emerge (first panel, arrow). Tgfβr2 was expressed predominantly in the dorsal area of the otic epithelium, including the endolymphatic duct anlagen (second panel, arrow). The presence of active TGFβ signalling was assessed with immunodetection of the phosphorylated downstream effector protein SMAD2 (pSMAD2), which showed a nuclear localization throughout the otic epithelium and the developing endolymphatic duct (third panel, arrow). (C) Tgfβ2 was strongly expressed in the developing endolymphatic duct at later developmental stages, HH20 and HH25 (arrows). Representative microphotographs are shown from at least three embryos per condition. Orientation: A, anterior; D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; R, rostral. Scale bars: 100 μm.