Figure 1.
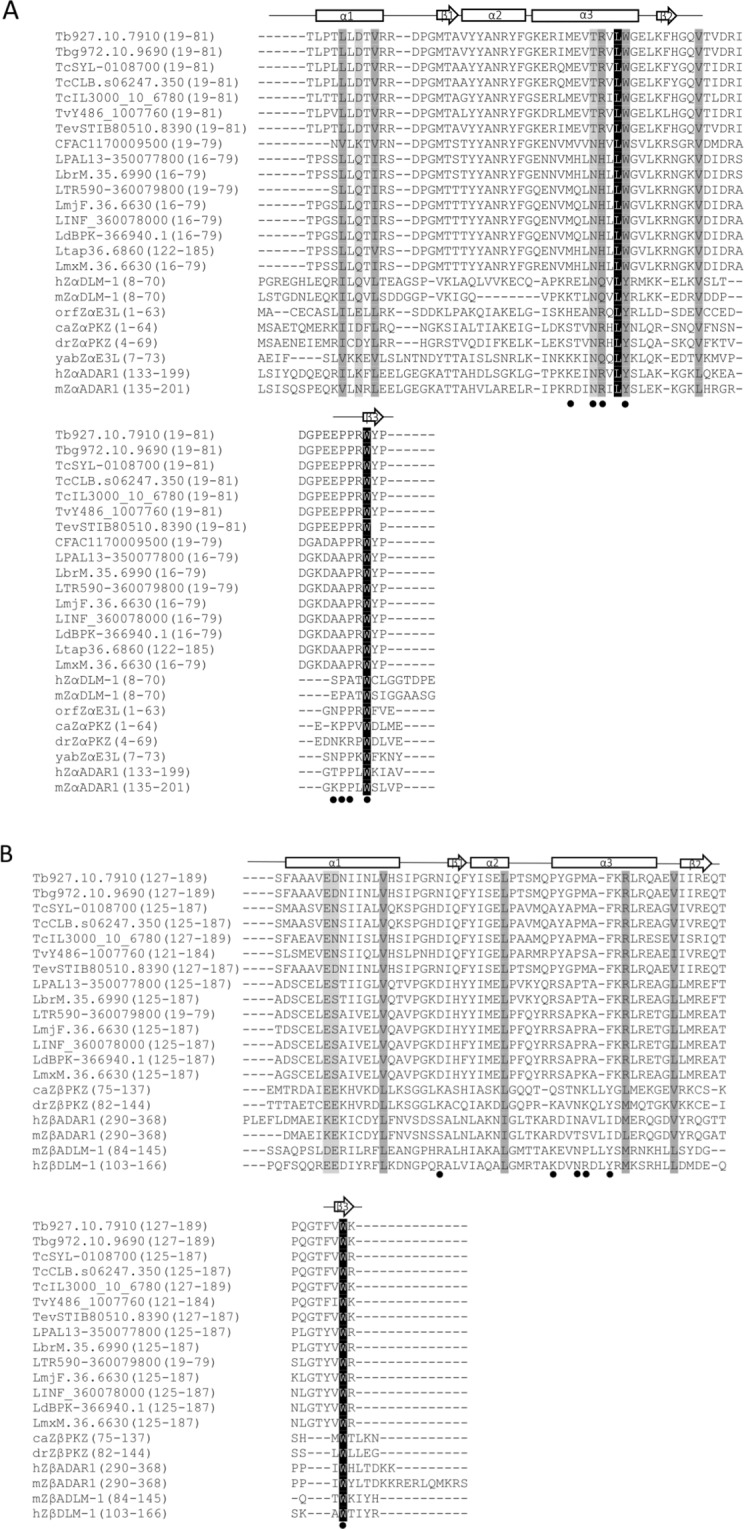
Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of predicted N- and C-terminal ZBDs of RBP7910 with Zα and Zβ domains of ZBPs, respectively. (A) Sequence conservation of the N-terminal ZBD of RBP7910, its orthologues from various kinetoplastid species, and Zα of other ZBPs and (B) sequence conservation of the C-terminal ZBD of RBP7910, its orthologues from various kinetoplastid species, and Zβ of other ZBPs. Predicted secondary structure of ZBD is indicated above the sequence of the first and second Z-domains of RBP7910. The α-helices are represented by tubes and β-strands by bold arrows. hZαADAR1 and hZβDLM-1-DNA interactions are marked with black circles. Shading from black to white corresponds to the degree of the amino acid conservation. Black shaded residues represent 100% identity. Numbers in parentheses correspond to the domain boundaries within the respective protein sequence. The sequences are as follows: RBP7910, kinetoplastid species, including T. b. gambiense, T. cruzi Sylvio, T. cruzi CL, T. congolense, T. vivax, T. evansi, Crithidia fasciculata, Leishmania panamensis, Leishmania braziliensis, Leishmania tropica, Leishmania major Friedlin, Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, Leishmania tarentolae, Leishmania Mexicana, and for Zαs; DLM-1 from Homo sapiens in hZαDLM-1 and Mus musculus, mZαDLM-1; E3L from orf virus in orfZαE3L and yabZαE3L from Yaba-like disease virus; PKZ from goldfish, caZαPKZ and drZαPKZ in zebrafish; ADAR1 from Mus musculus, mZαADAR1, and hZαADAR1 in Homo sapiens. Zβs include goldfish PKZ, caZβPKZ and zebrafish PKZ, drZβPKZ; ADAR1 in hZβADAR1 from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus, mZβADAR1; DLM-1 in Mus musculus, mZβDLM-1, and hZβDLM-1 from Homo sapiens.
