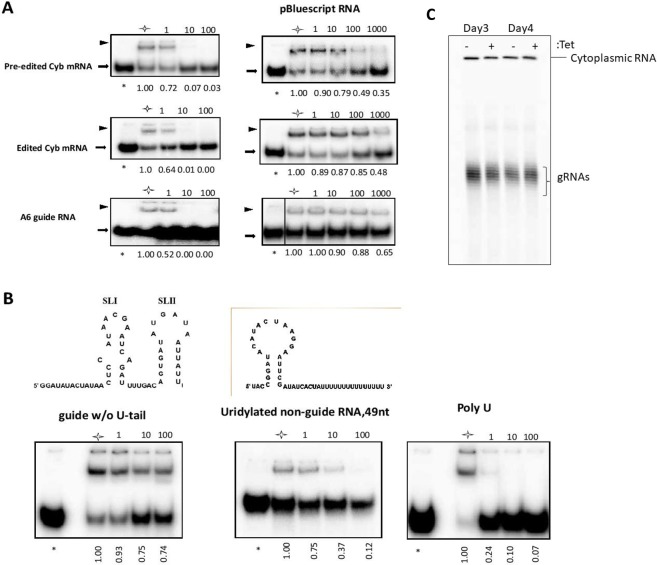
Figure 3.
Competition assays to determine the binding specificity of RBP7910 for CYb pre-edited and edited RNAs and gA6[14] RNA. (A) RBP7910 protein was individually incubated with labeled pre-edited CYb, edited CYb, and gA6[14] RNAs in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of each related unlabeled RNAs as a competitor. Labelling of the panels in this figure follow the same order as Fig. 2. Left panel, same as A; except that it uses a different competitor, pBlueScript RNA. (B) Competition assays to determine the role of gRNA oligo (U)-tail and stem-loop structure in gRNA binding. Three different competitors were examined to clarify the role of the oligo (U)-tail and the secondary structure of the gRNA in RBP7910 binding including gA6 RNA without the oligo (U)-tail, uridylated non-guide RNA with one predicted stem-loop and an oligo (U)-tail, and poly-U RNA. A fixed concentration of RBP7910 was incubated with labeled gA6[14] in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of unlabeled competitors. (C) The effect of RBP7910 RNAi silencing on gRNAs. RNAs from Tet-induced and uninduced RBP7910 RNAi 3d and 4d post-induction were capped with [α-32P] GTP by the recombinant guanylyltransferase enzyme. The population of small gRNA molecules was resolved as a ladder of bands on a denaturing 8% acrylamide/7 M urea gel (bottom panel). A cytosolic RNA (top panel) is simultaneously labeled by this reaction and is shown as a loading control.