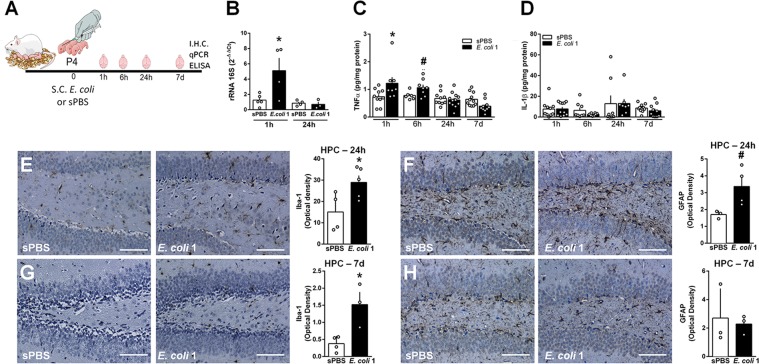
Fig. 2. Neonatal E. coli infection induces transient hippocampal inflammation and astro- and microgliosis.
a Swiss pups received a s.c. injection of sterile PBS (sPBS) or E. coli 1 × 104 CFU/g (E. coli 1) at post-natal day 4 (P4), and brains were collected 1, 6, 24 h or 7 days later. b qPCR for gamma-proteobacteria rRNA 16 S was performed in whole brains of mice 1 or 24 h after s.c. injection of E. coli or sPBS, and normalized by actin. TNF-α (c) and IL-1β levels (d) were measured in brains of mice at different timepoints after s.c. injection of E. coli or sPBS. e, g Representative images of Iba-1 immunoreactivity in the DG hippocampal region of mice 24 h (e) and 7 days (g) after s.c. injection of E. coli 1 or sPBS. Graphs show integrated immunoreactivity (optical density) for Iba-1 in the hippocampus. f, h Representative images of GFAP immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of mice 24 h (f) and 7 days (h) after s.c. injection of E. coli 1 or sPBS. Graphs show integrated immunoreactivity (optical density) for GFAP in the hippocampus. Scale bars = 50 µm. In (b): *p = 0.037, in (c): *p = 0.0449, #0.0576, in (e): *p = 0.037, in (f): #p = 0.0575, in (g): *p = 0.0189, Student’s t test