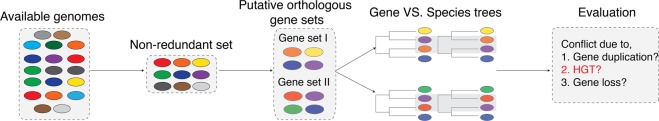
Figure 1.
HGT detection workflow. From a large pool of available completely sequenced genomes, non-redundant genomes are filtered and selected for downstream analysis. Putative orthologous gene sets and corresponding reference species trees are then reconstructed based on different criteria (e.g. NJ, ML, and other approaches16). Gene sets are called ‘putative’ orthologs as they are subjected to downstream tests for HGT participation. Each gene-species tree pair is evaluated for topological incongruence (see the dark shaded area in trees). Tree conflicts can arise from any of the following gene family evolution events: (i) duplication, (ii) HGT, and (iii), gene loss, commonly known as the duplication-transfer-loss (DTL) problem20. Out of the most parsimonious reconciliation (in terms of total cost of gene family evolution events)20, conflicts arising from transfer are stored for further analysis.