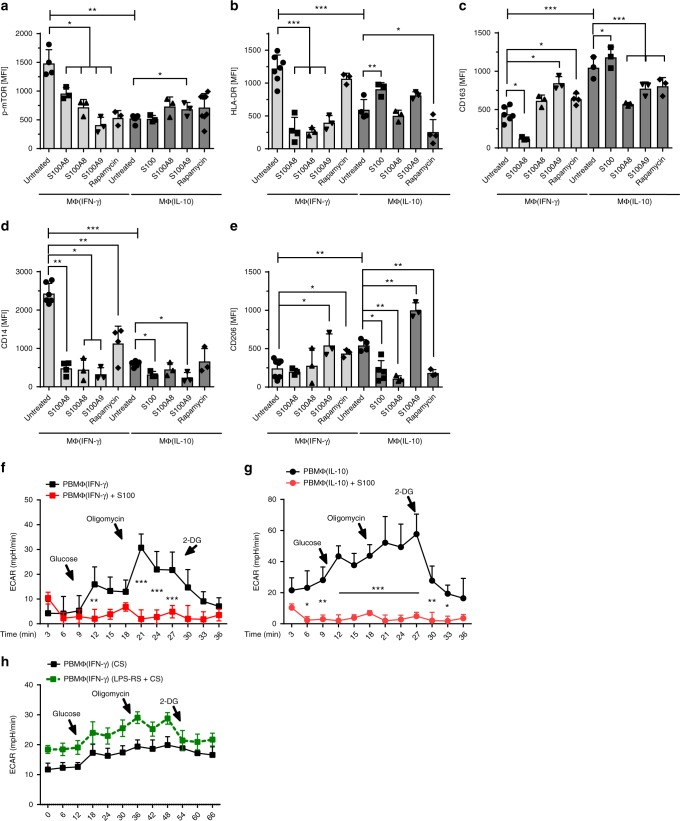
Fig. 6.
S100A8/A9 downregulates p-mTOR, activation markers, and glycolysis in PBMΦ. Bar diagrams show expression of pmTOR (a), expression of MΦ(IFN-γ) surface proteins (HLA-DR and CD14) (b, d) and MΦ(IL-10) surface proteins CD206 and CD163 (c, e) in untreated macrophages and macrophages treated either with S100A8 or S100A9 or treated with both simultaneously or treated with rapamycin. Polarization was induced in PBMC using 100 ng/ml hM-CSF for 72 h in RPMI in the presence or absence of 5 µg/ml S100A8 or A9. Further polarization was achieved by addition of 50 ng/ml IFN-γ MΦ(IFN-γ) or 10 ng of IL-10 MΦ(IL-10) for an additional 48 h. Immunotyping was performed by flow cytometric analysis detecting selected surface markers of mTOR, CD14, HLA-DR, CD163, and CD206. Significance of reduced expression in S100A8 or S100A9-treated MΦ was tested by utilizing the ANOVA test (indicated by blunt-ended bars) followed by Bonferroni post test (N = 3–8; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005). ECAR levels were measured after incubation of MΦ(IFN-γ) (f) and MΦ(IL-10)Φ with S100A8/A9 (g). ECAR levels were measured after incubation of MΦ(IFN-γ) with CB serum (CS) + /− LPS-RS. Points indicate mean from three to six experiments, error bars SEM (h). For detailed statistics see supplemental information