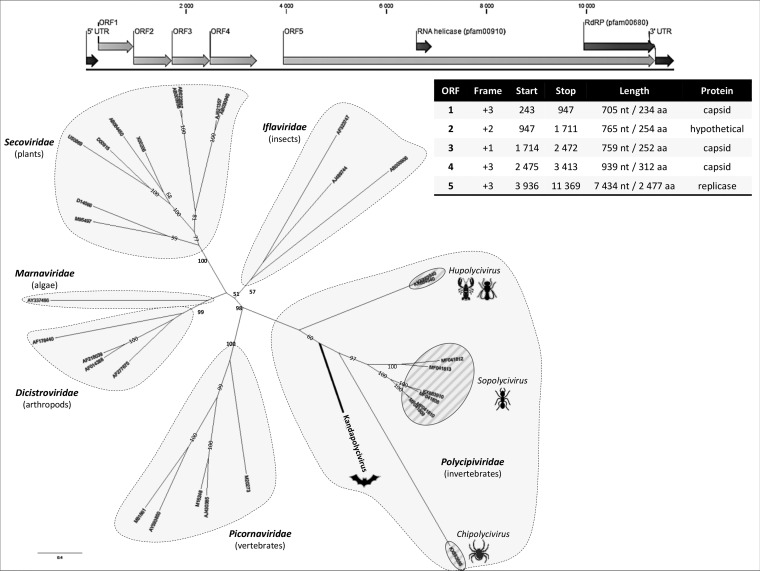
FIG 1.
Genome organization of Kandapolycivirus, phylogenetic analysis of polycipiviruses, and representative members of the Picornavirales order. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase domains were retrieved from Koonin et al. (2) and Olendraite et al. (3) with corresponding accession numbers presented on the tree. Complete amino acid sequences were aligned with MAFFT with the L-INS-I parameter (13). The best amino acid substitution models that fitted the data were determined with ATGC start model selection (14) implemented in PhyML with smart model selection (www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml-sms/) using the corrected Akaike information criterion. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) method implemented through the RAxML program under the CIPRES Science Gateway portal (15) according to the selected substitution model. Nodal support was evaluated using the “automatic bootstrap replicates” parameter. Supported nodes (i.e., with bootstrap values above 50) are represented, and bold type indicates nodes defining a family.