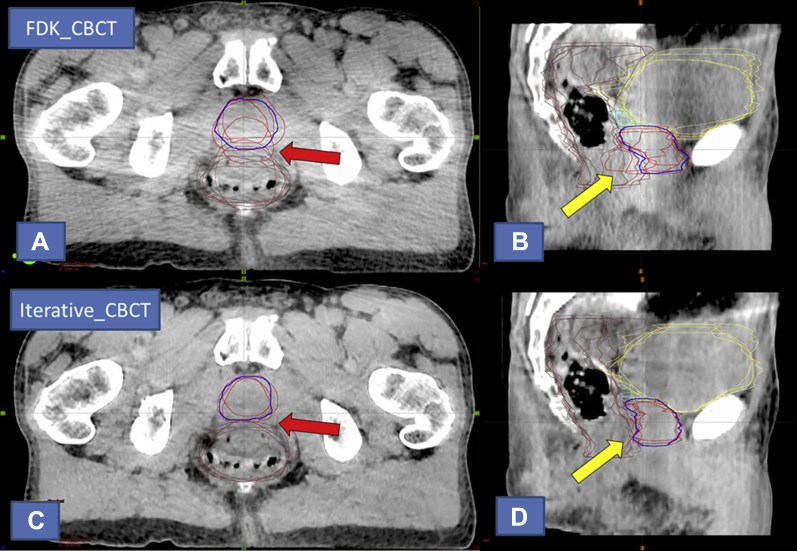
Fig. 2.
Visual contouring analysis for patient 5 of the prostate study, representing the largest Dice coefficient improvement for prostate contours. Prostate observer contours are shown in red and consensus contour in blue. Overall, the patient appeared to exhibit less inherent soft-tissue contrast than other patients within the study data set. (A) Axial and (B) sagittal views of the currently available algorithm (FDK_CBCT) reconstruction, respectively. Note the variation in the prostate-rectal interface on the axial (red arrow) and sagittal (yellow arrow) views of the contouring; (C) axial and (D) sagittal views of the novel iterative algorithm (Iterative_CBCT) reconstruction, respectively. Note the decreased noise and improved uniformity of the Iterative_CBCT image set relative to FDK_CBCT in both views. Also note the improvement in delineation of the prostate-rectal interface in both views relative to the FDK_CBCT image.