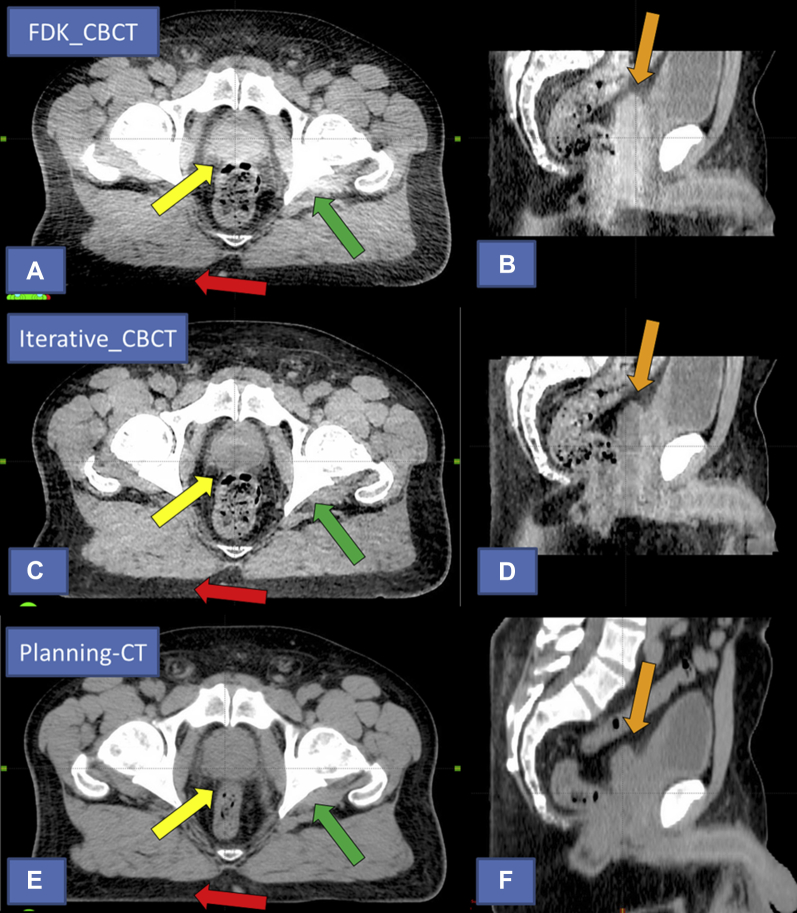
Fig. 3.
Comparison of image quality for prostate patient 4. Top images (A) and (B) currently available algorithm (FDK_CBCT). Middle images (C) and (D) novel iterative algorithm (Iterative_CBCT). Bottom images (E) and (F): Planning computed tomography (acquired on different day than the cone beam computed tomography [CBCT] data sets). Note the improvement in image intensity homogeneity in the peripheral portion of the axial field of view (FOV; red arrow), central portion of the axial FOV (yellow arrow), and central portion of the sagittal FOV (orange arrow) in the Iterative_CBCT image. Also note the improved sharpness and image intensity uniformity near bony anatomy (green arrow) and the improved overall image noise for the Iterative_CBCT data set.