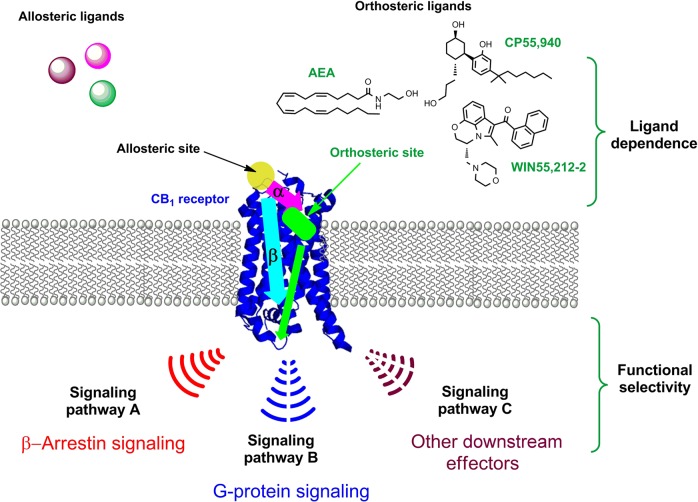
Fig. 10.
Schematic illustrating GPCR allosteric modulation and functional selectivity. Allosteric modulators alter the binding affinity (a: pink arrow) and/or efficacy (b: cyan arrow) of orthosteric ligands in a positive (PAM) or negative manner (NAM). Allosteric modulation often shows ligand dependence (i.e., different orthosteric ligands induce different forms of allostery). An allosteric modulator induces the receptor to adopt various conformations that preferentially activate either G-protein-mediated or a β-arrestin-mediated signal transduction. Other downstream effectors may also be preferentially involved in signaling pathways at the expense of others (functional selectivity). The resulting functional selectivity might generate a pharmacologically improved therapeutic effect, with reduced on-target adverse effects compared to the orthosteric ligand