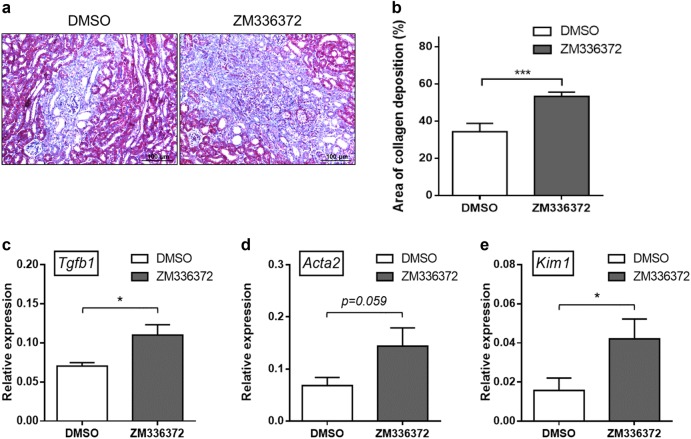
Fig. 9.
Inhibition of Raf-1 activation increases collagen deposition, TGF-β1 expression, and worsens renal damage. C. albicans (1 × 105)-infected hDC-SIGN transgenic mice were given Raf-1 inhibitor (ZM336372) (25 mg/kg) or DMSO intravenously on days 0, 1, 3, and 5 after infection. Mice were perfused with PBS and the kidneys were collected on day 6. a Paraffin-embedded kidney sections were stained with Masson’s trichrome stain to assess collagen deposition. Collagen fibers were stained blue. Original magnification, ×200. Scale bar = 100 µm. b The area of collagen deposition was analyzed by the Tissue Studio software. Ten regions per section were analyzed. Percentage of the area of collagen deposition (%) was calculated as [collagen-positive area (blue)/(collagen-positive area + collagen-negative area)] × 100%. The mean percentages of the area of collagen deposition are shown. The bars represent the mean ± SEM. c–e The levels of c Tgfb1, d Acta2, and e Kim1 in the kidney were quantified by qPCR and normalized against Gapdh. The bars represent the mean ± SEM. n = 3 for each group. b–e Data were analyzed by Student’s two-tailed t test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001