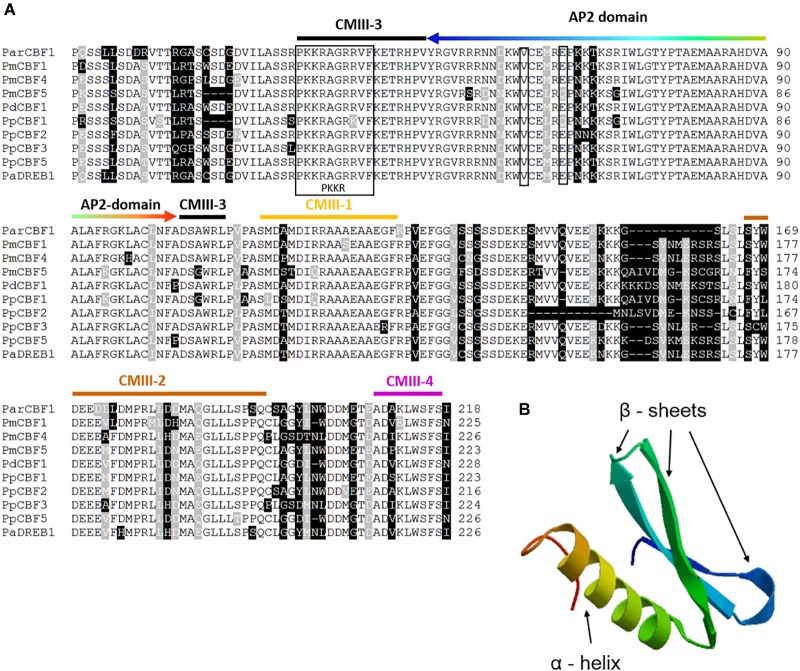
FIGURE 1.
Sequence alignment of Prunus C-repeat Binding Factors (CBF) and the structure of Prunus armeniaca CBF1 protein. (A) Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of P. armeniaca CBF and other Prunus CBF sequences. Dashes indicate gaps introduced to optimize the alignment. Identical amino acids and conserved substitutions are shaded black and gray, respectively. The total number of amino acids for each deduced protein is indicated at the end of each sequence. The PKKR/PAGR nuclear localization signal and the DSAWR motif are indicated by a black frame. Further CBF signature sequences are marked by orange (CMIII-1), brown (CMIII-2), black (CMIII-3) and purple (CMIII-4) colored stripes over the sequence motifs. The DNA-bindig AP2 domain is indicated by a rainbow-colored arrow (the order of colors indicate identical amino acid positions in the alignment and ribbon diagram in B), two narrow frames point to the two important amino acids responsible for DNA-binding specificity (a valine and a glutamic acid in the positions 14th and 19th, respectively). The CBF sequences and their GenBank accession numbers or references are as follows: ParCBF1 (MH464453) from P. armeniaca L.; PmCBF1, PmCBF4 and PmCBF5 from P. mume published in Zhao et al., 2018; PdCBF1 (KJ818900) is from P. dulcis; PpCBF1 (HM992943), PpCBF2 (KC543498), PpCBF3 (KC543499), and PpCBF5 (KC543501) from P. persica; and PaDREB1 (AB121674) from P. avium. (B) Molecular model of the AP2 domain (http://swissmodel.expasy.org). AP2 domain consists of three β-sheets and an α-helix.