FIGURE 1.
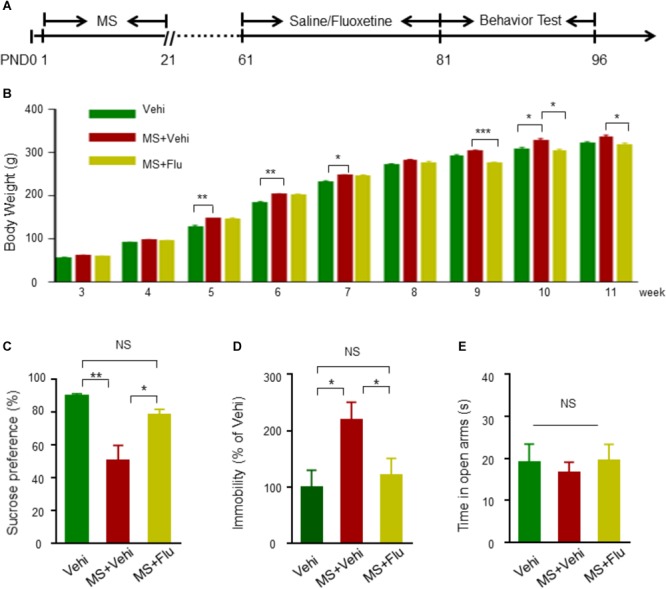
Neonatal MS induced depression-like behavioral deficits in adult Wistar rats. (A) The experimental schedule of MS, Fluoxetine administration, and behavioral test. Fluoxetine 10 mg kg-1 i.p. administration when rats were 8 weeks old before behavioral assessment at 11 weeks old. (B) Animals in all subgroups were weighted on the 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th, 9th, 10th, and 11th postnatal weeks (n = 11 rats per group). (C) Reduced sucrose preference rate by rats with MS in SPT test compared to Vehi group rats, and the reduction was diminished after Fluoxetine administration (n = 11 rats per group, F(2,30) = 30.82, one way-ANOVA). (D) Elevated immobility time in rats with MS+Vehi compared to Vehi rats and the elevation was ameliorated by Fluoxetine administration (n = 11 rats per group, F(2,30) = 0.037, one way-ANOVA). (E) There was no difference on time in open arms in EMP test (n = 10–11 rats per group, F(2,28) = 1.086, one way-ANOVA). Data are expressed as the means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. NS, not significant.
