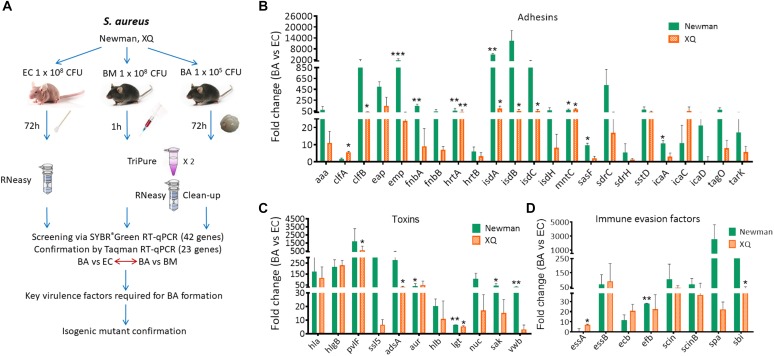
FIGURE 2.
RT-qPCR detection of the expression levels of virulence determinants in the murine models of BA and EC. (A) Schematic of the experiment performed to identify key virulence determinants that contribute to the formation of BA induced by S. aureus. BALB/c-nu/nu or C57BL/6 mice were infected with the indicated dose of S. aureus Newman or XQ. Samples were then collected at 1 or 72 h after bacterial infection and subjected to SYBR®Green RT-qPCR for the detection of 42 virulence genes. The 23 genes of interest were further confirmed through TaqMan RT-qPCR analysis. The expression patterns of S. aureus genes in the BA model were compared with those in the EC and BM models. The functions of screened genes were further identified through isogenic mutant experiments. SYBR®Green RT-qPCR detection of virulence profiles. (B) Adhesin genes, (C) Toxin genes, and (D) Immune evasion factor genes in the mouse models of BA and EC. The transcript levels of genes were normalized to those of the 16S rRNA gene, and results for the BA model were compared with those for the EC model. The S. aureus strains Newman (green bars) and XQ (orange bars) were analyzed. Results are from three independent experiments with 10 animals/experiment. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).